New compound synthesised can combat aggressive breast cancer
New compound synthesised can combat aggressive breast cancer
A newly designed nitro-substituted organoselenium compound can reduce the invasiveness of aggressive triple-negative breast cancer cells by modulating various signalling pathways.
Nature has inspired many drug discovery strategies, including design and synthesis. Organoselenium compounds, some sourced from plants and others synthesised in the lab are gaining attention for their biological activities. However, their ability to target interconnected oncogenic signalling networks has not been extensively studied, prompting research into their structural modifications and anticancer properties.
Research jointly led by Dr. Asis Bala, at the Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST), an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), GoI, and Dr. Krishna P. Bhabak, Department of Chemistry at IIT Guwahati, has successfully designed and synthesized an organoselenium compound 4-nitro-substituted benzylic diselenide 7.
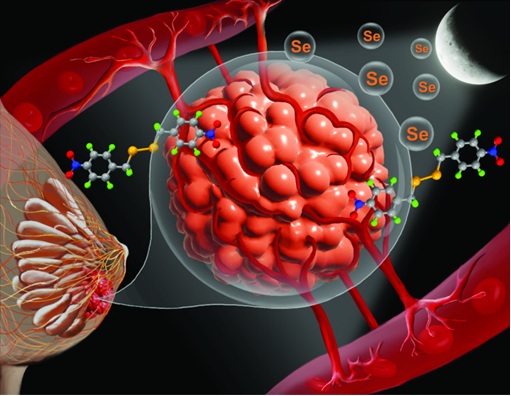
Figure: A schematic diagram illustrating the work completed.
The team synthesised it via nucleophilic substitution of benzylic halides with Na₂Se₂ and NaHSe, obtained by reducing elemental selenium with sodium borohydride under an inert atmosphere.
This newly synthesized nitro-substituted organoselenium compound, called diselenide 7, was found to reduce the invasiveness of aggressive triple-negative breast cancer cells by modulating various signaling pathways. In Swiss albino mice with breast adenocarcinoma, it significantly decreased tumour volume and reduced angiogenesis and metastasis, extending the animals’ lifespan.
Investigations revealed that the compound exerts its anticancer effect by targeting multiple survival mechanisms within cancer cells. This treatment blocks two important pathways, Akt/mTOR and ERK, that help cancer cells grow and are critical for uncontrolled cell growth. It also creates reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduces inflammation, which can damage DNA and harm the cancer cells, leading to cell death
This study highlights the role of nitro-substituted organoselenium compounds as multitargeting anticancer agents, supporting their development for effective cancer treatment.