Year End Review 2023-Ministry of Road Transport and Highways
Year End Review 2023-Ministry of Road Transport and Highways
A. NATIONAL HIGHWAYS: CONSTRUCTION & ACHIEVEMENTS
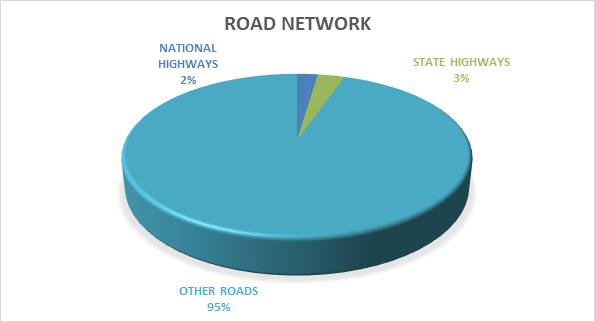
1. Road Network in the Country: India has about 66.71 lakh km of road network, which is the second largest in the world.
The length of various categories of roads is as under:
National Highways play a very important role in the economic and social development of the country by enabling efficient movement of freight and passengers and improving access to markets. MoRTH and its implementing agencies have undertaken multiple initiatives in last 9 years to augment the capacity of the National Highway infrastructure in India.
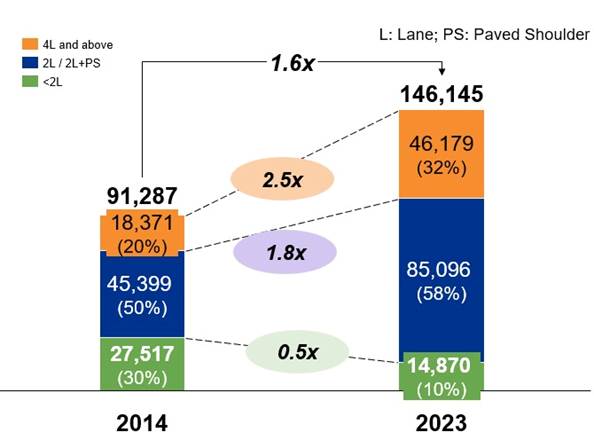
2. National Highway Network
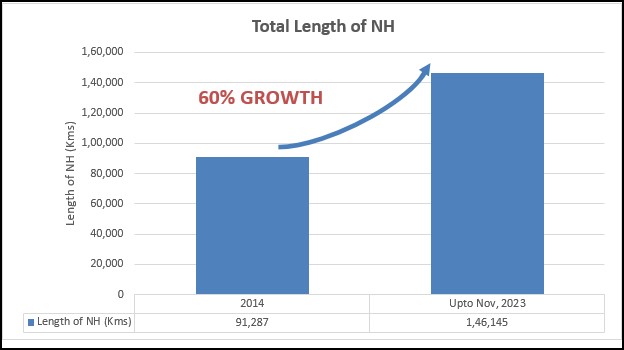
The length of National Highways (year-wise) is tabulated below:
Sr. No.
Year
Length (in km)
1
2013-14
91,287
2
2014-15
97,830
3
2015-16
1,01,010
4
2016-17
1,14,158
5
2017-18
1,26,500
6
2018-19
1,32,500
7
2019-20
1,32,995
8
2020-21
1,38,376
9
2021-22
1,41,345
10
2022-23
1,45,240
11
2023-24(up to Nov 2023)
1,46, 145
(Source- “Basic Road Statistics of India)
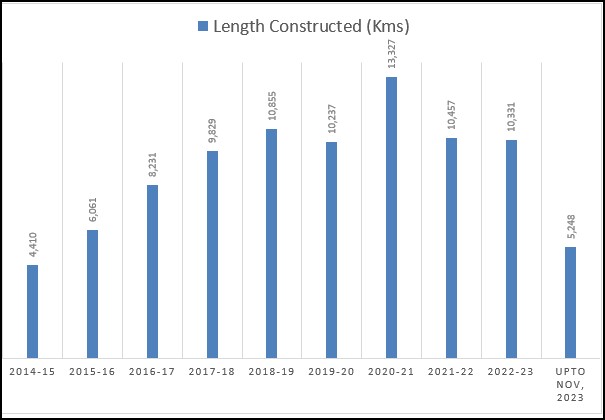
Length Constructed: MoRTH constructed 5248 km of National Highways. (Provisional figures).
The pace of National Highways (NH) construction has increased consistently between 2014-15 and 2023-24 due to the systematic push through corridor-based National Highway development approach.
Sr. No.
Year
Construction (in km)
Construction (in km / day)
1
2014-15
4,410
12.1
2
2015-16
6,061
16.6
3
2016-17
8,231
22.6
4
2017-18
9,829
26.9
5
2018-19
10,855
29.7
6
2019-20
10,237
28.1
7
2020-21
13,327
36.5
8
2021-22
10,457
28.6
9
2022-23
10,331
28.3
10
2023-24(up to Nov 2023)
5,248
–
2. Bharatmala Pariyojana: The Bharatmala Pariyojana was launched with the primary focus on optimizing the efficiency of the movement of goods and people across the country. Phase I of the Bharatmala Pariyojana approved in October 2017, focuses on bridging critical infrastructure gaps through development of 34,800 km of National Highways. The Pariyojana emphasised a “corridor based National Highway development” to ensure infrastructure symmetry and consistent road user experience. The key components of the Pariyojana are Economic Corridors development, Inter-corridor and feeder routes development, National Corridors Efficiency Improvement, Border, and International Connectivity Roads, Coastal and Port Connectivity Roads and Expressways.
Status of Bharatmala Pariyojana Phase 1:
The status of Bharatmala Pariyojana Phase 1 entails a total length of 34,800 km in 31 States and UTs, 550+ Districts. The length awarded is 27,384 km and the length constructed is 15,045 km.
The phase 1 is to be completed by 27-28.
3. Relief for Contractors/Developers of the Road Sector in view of the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Ministry provided/extended the relief measures in view of the Covid-19 pandemic:
(i) Extension of relaxation in Schedule H/G till 31st March 2024 to improve the liquidity of funds available with the Contractors and Concessionaire.
(ii) Arrangement regarding direct payment to approved Sub-Contractor through Escrow Account may be continued till 31st March 2024 or the completion of the work by the Sub-Contractor, whichever is earlier.
(iii) Reduction of Performance Security/release of retention money: Reduction of Performance Security/release of retention money: This Ministry has already decided to reduce Performance Security from existing 5–10 % to 3% of the value of the contract for all existing contracts (excluding the contracts under dispute wherein arbitration/court proceedings have already been started or are completed). All tenders/contracts issued/ concluded till 31.03.2024 should also have the provision of reduced performance security. However, in order to ensure the quality of work being executed, the Ministry will advise all project executing agencies to ensure that in case of abnormally low bids (ALBs), additional performance security is realized as per the latest guidelines provided by the Department of Expenditure, Ministry of finance. Retention money is a part of the Performance Security till the construction period. Hence, the release of retention money may be continued in proportion to the work already executed and no reduction of retention money may be made from the Bills raised by the Contractor till 31.03.2024.
For HAM/BOT Contracts, a Performance Guarantee may be released on a pro-rata basis, as provided in the Contract if Concessionaire is not in breach of the Contract.
Changes in the Model Concessionaire Agreement (MCA) & Request for Proposal (RFP) of the road construction models: –
(i) Change in MCA for HAM projects to allow for flexible pavement including structures. Changes have been made in the RFP and MCA of HAM project to allow Lowest Quoted Bid Project Cost (BPC) as the basis for awarding HAM Project and cost to be fixed as in EPC projects. The changes in Clause 23.7 of MCA of HAM project issued by MoRTH included following three categories:
a) For flexible perpetual pavement including structures
b) For rigid pavement with 10-year maintenance period including structures
c) For stand-alone Bridges/Tunnel works
(ii) Inclusions of provisions regarding accepting Insurance Surety Bonds and e-bank guarantee as “Bid Security and Performance Security” in standard documents of EPC, HAM, and BOT (Toll):
Department of Expenditure vide Office Memorandum No. F. 1/4/2022-PPD dated 05.08.2022 made amendments in the Rule 170(i) and Rule 171(i) of General Financial Rules (GFR), 2017 to include e-bank guarantee as a means to accept Bid Security and Performance Security. Further, Department of Expenditure had amended Rule 170 (i) and Rule 171 (i) of GFR, 2017 to accept provision of Insurance Surety Bond as a mean of ‘Bid.
Security’ and ‘Performance Security’ vide OM dated 02.02.2022. The latest Circular issued by Department of Expenditure, O.M No. F. 1/2/2023- PPD dated 03.04.2023, also provides for Insurance Surety Bonds and e-bank guarantee as possible means of furnishing Performance Security. In view of this, necessary amendments were made in the standard documents of EPC, HAM, and BoT (Toll) by the Ministry.
4. Asset Monetization:
B. MAJOR EVENTS OF 2023
(i) INAUGURATIONS / LAYING OF FOUNDATION STONE BY PRIME MINISTER SHRI NARENDRA MODI
(Total: Rs. 59,650 Cr. approx.)
(ii) INAUGURATIONS / LAYING OF FOUNDATION STONE BY MINISTER RT&H SHRI NITIN GADKARI
(Total: Rs. 1,31,993.68 Cr. approx.)
(iii) Special Campaign 3.0 for disposal of Pending Matters:
The Ministry of Road Transport and highways has successfully implemented the special campaign 3.0 from 02.10.2023 to 31.10.2023. Identified targets under various parameters of the campaign and achievements made against them are as under:
S. No
Parameters
Target
Achievements
1
References from MPs
799
799
2
Public Grievances
764
764
3
Public Grievance Appeals
334
334
4
PMO References
18
18
5
Record Management
18013
18013
6
Cleanliness Campaign
13168
13168
7
State Govt. References
11
10
8
Revenue from Scrap Disposal
–
Rs 6, 31, 629
9
Space Freed
–
1,070 square feet
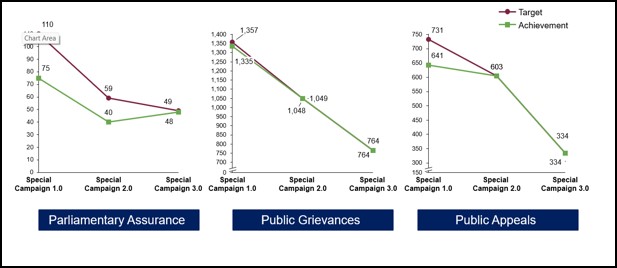
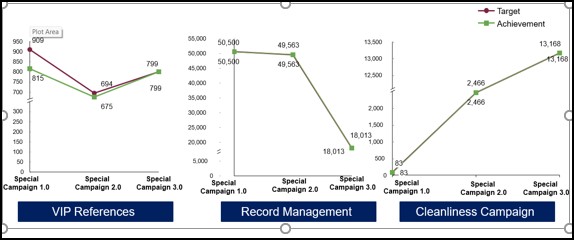
Pending Parliament Assurances, VIP References. Public Grievances & Public Appeals have steadily declined since SCDPM 1.0
OTHER EVENTS
C. ROAD TRANSPORT
Road transport is the dominant mode of transport in India, both in terms of traffic share and contribution to the national economy. Apart from facilitating the movement of goods and passengers, road transport plays a key role in promoting equitable socio-economic development across regions of the country. It also plays a vital role in social and economic integration and development of the country. Easy accessibility, flexibility of operations, door-to-door service and reliability have earned road transport a greater significance in both passenger and freight traffic vis-à-vis other modes of transport.
Strengthening ITS in Public Transport System
The Ministry has revamped its previous ITS Scheme and issued guidelines on June 23rd, 2022, to continue the previous scheme. This will provide additional financial support to STUs to equip themselves with advanced ITS technologies, improved bus services, operations, performance, and customer conveniences. The Scheme provides support of hardware and software components for Fleet Management System, Electronic Ticketing & Fare Collection System (including NCMC) and Passenger Information & Feedback System.
So far, proposals amounting to over Rs 250 crores have been received in the Ministry from several STUs such as TSRTC, KSRTC, GSRTC, APSRTC, Sikkim SNT, BMTC, Puducherry PRTC, Assam ASTC, Chandigarh CTU, MBMTU, Ahmedabad Janmarg Ltd., Bhopal City Link Ltd., NMMT, Kerala SRTC etc. A total of 5 proposals of TSRTC, KSRTC, GSRTC, BCLL and SNT amounting to Rs.122.49 Crores. Appraised and sanctioned. The rest of the other proposals are under consideration by this Ministry and several of them are already in the advanced stages of appraisal.
(i) CITIZEN-CENTRIC MEASURES
This facility is provided only for new registration of vehicles through Dealer point registration. This vehicle registration facility under “Bharat series (BH-series)” is available on voluntary basis to Defense personnel, employees of Central Government/ State Government/ Central/ State Public Sector Undertakings and private sector companies/organizations, which have their offices in four or more States/Union territories. Currently, BH series registration is active in 26 states Andaman & Nicobar Island, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chandigarh, Delhi, Goa, Gujarat, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Meghalaya Maharashtra, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, Odisha, Puducherry, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tripura, UT of DNH and DD, Uttarakhand ,Uttar Pradesh & West Bengal.
There is a gap in the emission performance when the same vehicle is tested in laboratory conditions and in real driving conditions. To reduce this gap, Real Driving Emission (RDE) regulations were introduced in Europe. In line with this, India also introduced RDE regulations along with the introduction of Bharat Stage VI (BS VI), making RDE measurement mandatory during type approval and COP. The said regulations are applicable from 1st April 2020 for data collection and from 1st April, 2023 for meeting Conformity factor (CF). CF defines the emission limits of the RDE regulations.
The Ministry of Road transport and Highways has mandated that the CF (conformity Factor) may be applicable, in respect of vehicles manufactured on and after 1st April, 2023 for all vehicles on real world driving cycle emission.
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) has notified the All-India Tourist Vehicles (Permit) Rules, 2023, superseding the All-India Tourist Vehicle (Authorization or Permit) Rules, 2021.
The rules notified in 2021 had provided a significant boost to the tourism sector in India by streamlining and simplifying the permit regime for tourist vehicles.
Now, with the All-India Tourist Vehicles (Permit) Rules, 2023, the All-India Tourist Permit (AITP) regime has been further streamlined and strengthened to provide greater ease of movement of tourist vehicles across the country.
The key features of the new rules are as follows:
a. To simplify the application procedure and to reduce compliance burden, the provision of authorization and AITP have been made independent of each other.
b. To promote deployment of electric vehicles and vehicles driven on methanol or ethanol fuel in large numbers, a streamlined regulatory ecosystem at no cost to the operator(s) has been introduced.
c. More categories of tourist vehicles, with lesser permit fees for lesser capacity vehicles (less than ten) have been introduced. This is expected to provide considerable financial relief to smaller tourist vehicle operators, having smaller vehicles with lower seating capacity, as they will now be required to pay lower fees commensurate with the seating capacity of their vehicle(s).
4. Fire Alarm System (FAS) and Fire Protection System (FPS) in Buses: –
This Ministry had extended the scope of AIS 135 from the engine compartment to include the passenger compartment of school buses and buses of Type III category amending CMVR for incorporating provision for fire protection of the passenger compartment of the buses. The implementation timeline was twelve months from the date of commencement of the Central Motor Vehicles (First Amendment) Rules, i.e. from 27th January 2023. The aim of this amendment is to provide an additional evacuation time to the occupants and thus to enhance the safety in fire incidents in buses through FPS and FAS. The standard was framed in consultation with various stakeholders including the experts of DRDO which had undertaken the design and had also tested the concept on a bus.
After receiving the representation from automotive stakeholders, this Ministry has deferred the date of implementation to 1st October 2023.
5. Conversion of fully built vehicles into adapted vehicles for Divyangjan: –
This Ministry has facilitated Divyangjan in the conversion of fully built vehicles into adapted vehicles through temporary registration.
Adaptation of motor vehicles, as per the specific needs of Divyangajan, is often required to facilitate their mobility. Currently, such adaptation could either be carried out prior to registration of vehicle, by the manufacturer or his authorized dealer, or after the registration of vehicle in as-is form on the basis of permission received from registering authority.
To simplify this process, MoRTH has amended rules 53A and 53B of Central Motor Vehicles Rules (CMVR), 1989, to extend the facility of Temporary Registration for adaptation of motor vehicles. These amendments will further facilitate the driving of motor vehicles by Divyangjan and promote their inclusion in socio-cultural and economic activities.
6. Bharat New Car Assessment Programme (BNCAP): –
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has inserted a new rule 126E in CMVR (Central Motor Vehicles Rules), 1989 regarding the Bharat New Car Assessment Program (BNCAP). The following has been mandated: –
“126E. Bharat new car assessment programme. –
(1) The car assessment programme under this rule shall be applicable on the type of approved vehicles of category M1, manufactured or imported in the country on or after the 1st day of October 2023. Further, BNCAP shall be a voluntary program monitored by the Agency.
(2) On and from the 1st day of October 2023, the manufacturer or importer of motor vehicles shall apply in FORM 70A, to the designated agency, designated by the Central Government to get their motor vehicle examined and assessed for star rating in accordance with AIS:197.
(3) The cost of the motor vehicle for the purpose of assessment for star rating and the cost of such assessment shall be borne by the respective manufacturer or importer.
(4) The motor vehicles for the purpose of assessment shall be randomly selected by the designated agency, from the premises of the manufacturer, importer, or operational dealers of the manufacturer or importer, in accordance with AIS-197.
(5) The designated agency shall select any of the testing agencies, referred to in rule 126, for the assessment of the vehicles selected in sub-rule (2).
(6) The manufacturer or importer shall send the selected vehicles to the testing agency selected under sub-rule (4).
(7) The testing agency shall evaluate the vehicles in accordance with AIS-197 and submit the assessment report to the designated agency in FORM 70B.
(8) On examination and approval of the assessment report, the star rating of the vehicle shall be uploaded on the designated portal by the designated agency:
(9) Nothing in this rule shall apply to a vehicle exempted under rule 126.”.
It introduces the concept of safety rating of passenger cars and empowers consumers to take informed decisions. It will promote export worthiness of the cars produced by OEMs in the country and increase the domestic customer’s confidence in these vehicles. Additionally, the program will encourage manufacturers to provide advanced safety technologies to earn higher ratings.
7. Amendment in various Forms of Central Motor vehicles Rules, 1989: –
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has amended various Forms of Central MIotor vehicles Rules, 1989 to capture information w.r.t. permitted Sleeping capacity, Standing capacity and Seating Capacity (including Driver).
8. Type Approval of Compressed Gaseous Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles: –
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has inserted new rule 125M in CMVR, 1989 to provide norms for type approval of liquid or compressed gaseous hydrogen internal combustion engine vehicles. It has been prescribed that the safety and procedural requirements for type approval of internal combustion engine vehicles of M and N categories powered by liquid or compressed gaseous hydrogen shall be in accordance with AIS 195:2023, till corresponding BIS specification is notified under the Bureau of Indian Standard Act, 1986 (63 of 1986). Provided that the hydrogen fuel specifications for internal combustion engine vehicles shall be in accordance with IS 16061: 2021.
9. Type approval of electric power train vehicles and hybrid electric vehicle: –
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has inserted a new rule 125N in CMVR, 1989 regarding Type approval of electric power train vehicles and hybrid electric vehicle. The definition of Hybrid vehicles is available in various Automotive Industry Standards (AIS); but, till date, a standard definition has not been incorporated in CMVR, 1989. It was therefore necessary to incorporate a standard definition of pure electric and hybrid vehicles & its various types, in CMVR 1989. It may also be pertinent to point out that various State governments are providing incentives to electric and hybrid vehicles through their respective state EV policies. Hence, by virtue of the notification it has brought more clarity in the definition and categorization of pure electric and hybrid vehicles.
D. ROAD SAFETY
PREVENTIVE MEASURES
6. Safety and Security of Women Passengers (Projects under Nirbhaya Framework):
The Government of India has set up a dedicated fund under the Nirbhaya Framework being administered by the Department of Economic Affairs, M/o Finance. Standalone projects from the Government of Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation, Telangana State Road Transport Corporation and Bangalore Metropolitan Transport Corporation have been approved under the Nirbhaya Fund Scheme to augment safety and security of women in public road transport, which are under different stages of execution.
7. Development of State-wise vehicle tracking platform in States/ UTs (under Nirbhaya Framework):
Ministry of Road Transport & Highways has approved a scheme (on 15th January 2020) for implementation of “Development, Customization, Deployment and Management of State-wise vehicle tracking platform for Safety & Enforcement as per AIS 140 Specifications in States / UTs under Nirbhaya Framework” at total estimated cost of Rs. 463.90 Crore (including Central and State share, as per Nirbhaya Framework).
MORTH has received proposals from 33 States/UTs. It has released funds amounting to Rs.213.88 Crore. So far, Eleven States/UTs i.e. Himachal Pradesh, Puducherry, Bihar, West Bengal, Sikkim, Uttarakhand, Mizoram, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Chandigarh and Andaman & Nicobar have commissioned the monitoring Centres and it is expected that more States/UTs are soon to follow the suit
E. VEHICLE SCRAPPING POLICY
Introduction: The “Vehicle Scrapping Policy” launched in August 2021 is aimed at creating an eco-system for phasing out of unfit and polluting vehicles in an eco-friendly manner. The policy targets voluntary scrapping of unfit commercial and personal vehicles strictly based on their fitness, irrespective of vehicle age. The policy offers multiple benefits such as reducing pollution, boosting availability of raw materials, promoting circular economy, improving road and passenger safety, boosting auto sector sales, and generating employment.
Rules and Notifications: MoRTH has notified rules and amendments for setting up automated fitness testing stations and registered vehicle scrapping facilities in consultations with industry and other stakeholders. In 2023, to provide an initial policy impetus, it was notified vide GSR 29 (E) on 17th January 2023 that the certificate of registration of Government-owned vehicles shall expire after the lapse of 15 years. Such vehicles shall be mandatorily scrapped at RVSFs. There was a special focus on scrapping and replacement of public service vehicles (buses, ambulances, fire tenders and police vehicles) for the benefit of the citizens.
Further, GSR 663 (E) dated 12th September 2023 provides for extension of date for mandatory testing of Transport Vehicles through ATSs, to 01st October 2024. However, where the automated testing station is operational in the jurisdiction of a registering authority, the fitness of the vehicle shall be done only through such automated testing station with immediate effect.
Policy Implementation Status: For successful implementation, a network of Automated Testing Stations (ATSs) and Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities (RVSFs) is required to be set up across India.
37 ATSs operationalised across 8 States so far, of which 35 were operationalised in 2023.
 Concession in Motor Vehicle (MV) Tax for vehicle registered against Certificate of Deposit: Announced by 19 States / UTs so far, of which 9 States / UTs have announced the incentive in 2023.
Concession in Motor Vehicle (MV) Tax for vehicle registered against Certificate of Deposit: Announced by 19 States / UTs so far, of which 9 States / UTs have announced the incentive in 2023.
Waiver of Registration Fees for vehicle registered against Certificate of Deposit: Announced and Implemented Pan-India.
Waiver of pending liabilities (e.g., pending tax, interest, fines etc.): Announced by 16 States / UTs so far, of which 14 States / UTs have announced the incentive in 2023.
Around 49,700 vehicles scrapped till date at RVSFs of which ~ 39,200 vehicles scrapped in 2023 till date across Government-owned and Private vehicle categories. Government owned vehicles, ~30,400 scrapped till date of which ~26,600 have been scrapped in 2023.
Incentive Scheme for States: To increase the pace of implementation of the Vehicle Scrapping Policy, incentives worth INR 2,000 Cr. was extended to State Governments for FY22-23 under Department of Expenditure’s ‘Scheme for Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment’ on 16th December 2022. The Department of Expenditure has approved the incentives worth Rs 351 Crores for the States of Uttar Pradesh, Assam, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, and Odisha as per proposals submitted for FY 2022-23.
The Scheme for Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment has been extended for the financial year 2023-24 by the Government and the incentive amount to the States has been increased to Rs. 3000 crores, to incentivize scrapping of State Government vehicles which are older than 15 years, waiver of liabilities on old vehicles, providing tax concessions to individuals for scrapping of old vehicles and setting up of automated vehicle testing facilities.
Under the scheme for FY 2023-24, proposals from Punjab, Haryana, Kerala, Chhattisgarh, Bihar, Uttarakhand, Mizoram, and Karnataka have been received after completion of activities under Milestone 1 of Part A Of the scheme in 2023-24. The Department of Expenditure has approved the incentives worth Rs 62.5 Crs for the States of Punjab and Bihar as per proposals submitted.
Digitization: For smooth operations amongst various stakeholders of the policy ecosystem, two key IT infrastructure portals has been enabled for State Government, Investors and End Users
RVSF portal: NIC has developed a module on Vahan through which vehicle owners can submit application to scrap end-of-life vehicles.
(ELV). New features added for RVSFs (bulk upload of government vehicles) and citizens (self-backlog entry for vehicles not on Vahan, dedicated helpdesk operating on all 7 days).
F. LOGISTICS & ALLIED HIGHWAY INFRASTRUCTURE
1. MULTI MODAL LOGISTICS PARKS (MMLPs)
The Ministry finalized the Model Concessionaire Agreement (MCA) for the MMLPs to be developed under the Bharatmala Pariyojana in October 2021 through an elaborate process of inter-Ministerial consultations. The document serves as the Developer Agreements/ Concession Agreements for the individual MMLP projects under the Pariyojana. In addition to the MCA, the Ministry, in November 2021, also finalized and approved the Model RFP document of selection of Concessionaire for development of MMLPs.
A network of 35 Multimodal Logistics Parks is planned to be developed as part of Bharatmala Pariyojana, with a total investment of about Rs 46,000 crore, which once operational, shall be able to handle around 700 million metric tonnes of cargo. Of this, MMLPs at 15 prioritized locations will be developed with a total investment of about Rs 22,000 Crore.
These Multi-Modal Logistics Parks shall serve as regional cargo aggregation and distribution hubs for various industrial and agricultural nodes, consumer hubs and EXIM gateways such as seaports with multi-modal connectivity. In certain cases, the MMLPs are also being developed in tandem with the Inland Waterway Terminals under the Sagarmala Pariyojana to further reduce the cost of inland cargo movement at a much larger scale as compared to conventional road-based movement.
(i) MMLP Jogighopa (Assam) in advanced stage: Execution of enabling development work including road, rail & water connectivity, area development such as site leveling, boundary work, internal road, administrative building, STP, WTP etc. is in advance stage.
Procurement of developer on PPP basis (Concession Period: 45 years) for construction of Logistics facilities such as business centre, container yard, warehouses, cold storage, etc. and operations thereof subsequently is in process.
The estimated cost of the first phase of the project is 693.97 crore. The foundation stone of the project was laid in October 2020 by Hon’ble Minister (RT&H) Shri Nitin Gadkari. This MMLP will serve as the distribution centre for all North-Eastern states and facilitate cross-border trade with Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal.
(ii) Work Awarded for 4 MMLPs:
Details of awarded MMPLs.
S.No
MMLP
State
Location
Land
(Acres)
Investment
(Rs., Cr)
Date of Award
1
Chennai
Tamil Nadu
Mappedu
184
1,424
11-Nov- 2022
2
Indore
Madhya Pradesh
Pithampur
255
1,110
28-Feb- 2023
3
Bangalore
Karnataka
Dabbaspete
400
1,770
16-May- 2023
4
Nagpur
Maharashtra
Sindi
150
673
10-Nov-2023
These projects, when completed, will contribute significantly to the growth of India’s logistics sector with reduction in carbon emission and strengthen the country’s infrastructure.
(iii) Bids invited for 2 MMLPs i.e., at Anantapur and Pune. The work of preparation of Feasibility Study Reports is in progress for MMLP at Coimbatore, Hyderabad, Visakhapatnam, Nashik, Mumbai, Jammu and Patna.
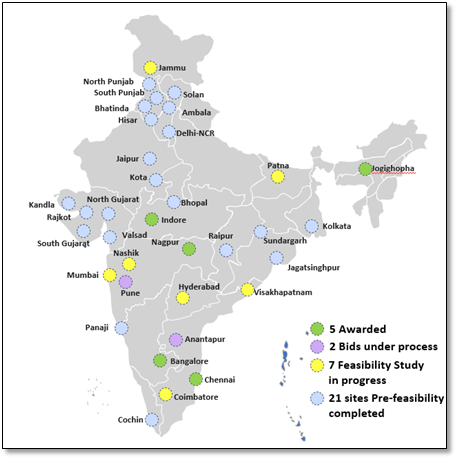
Figure: Status of MMPLs
2. PORT CONNECTIVITY
India currently has 87 Operational and Under Implementation ports along its coastline. All Major operational ports currently have 4 lane and above last mile road connectivity.
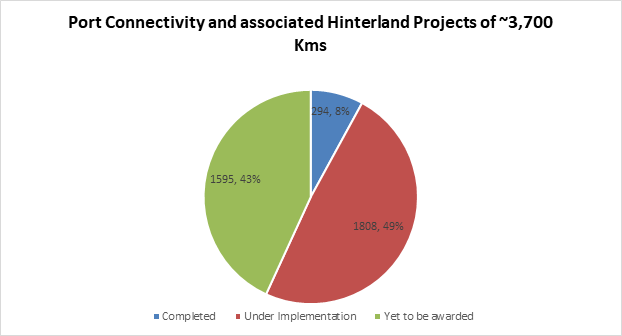
MoRT&H and its implementing agencies have planned the development of 108 Port Connectivity Road (PCR) projects of length ~3,700 km to improve the last mile connectivity of all 87 Operational and Under Implementation ports.
The formulation and selection of these projects have arisen from a collective decision-making process that involved the Ministry of Road, Transport, and Highways, the Ministry of Port Shipping and Waterways, and the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT). These deliberations adhered to the fundamental principles of PM Gati Shakti, reinforcing the commitment to expedite infrastructure development and promote seamless connectivity in the country.
Of the 108 PCR projects under the Ministry
• 8 projects of length 294 km have been completed
• 28 projects of length 1808 km are awarded and under various stages of implementation
• And 72 projects of length 1595 km are balance for award
3. WAY SIDE AMENITIES
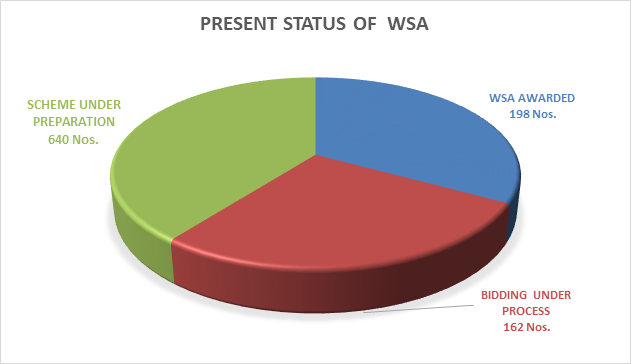
To improve the comfort and convenience of the Highway users, the Ministry has planned the development of state-of-the-art Wayside Amenities (WSA) at about every 40 kms along the National Highways on PPP mode. These facilities are aimed to provide multiple options of rest and refreshment for the highway commuters during their journey. Some of the mandatory facilities being developed at each WSA are fuel stations, EV charging stations, food court / restaurants, dhabas, convenience stores, clean and hygienic toilet facilities, drinking water, first aid / medical room including childcare room, dedicated area for promoting local artisans, car/bus/truck parking, drone landing facilities / helipad etc.
A total of 1000+ sites are planned to be awarded by 2024-25 of which 198 Wayside Amenities (WSAs) have already been awarded. 162 WSAs are under bidding stage. These WSAs will offer huge opportunities for investors, developers, operators and retailers. All upcoming Greenfield Access-controlled Highway projects are provisioned to have Wayside Amenities essentially, which will also promote local economy by generating employment opportunities and help local people to market their unique produces/ handicrafts etc. at village haats developed at these places.
4. UTILITY CORRIDORS
Working towards development of around 10,000 km of Optic Fibre Cables (OFC) infrastructure across the country by FY2024-25, National Highways Logistics Management Limited (NHLML), a fully owned Company of NHAI, is implementing the network of Digital Highways by developing integrated utility corridors along the National Highways to develop OFC infrastructure. Around 1,367 km on Delhi – Mumbai Expressway and 512 km on Hyderabad – Bangalore Corridor have been identified for the Digital Highway Development.
G. TOLL
Ø In order to ensure seamless movement of traffic through fee plazas and increase transparency in collection of user fee using FASTag, the National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) programme, the flagship initiative of Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, has been implemented on pan-India basis. The National Payment Corporation of India (NPCI) is the Central Clearing House (CCH). There are thirty-Nine (39) banks (including Public and Private sector banks) engaged as issuer banks for FASTag issuance to road users and fourteen (14) acquirer banks to process the transactions at fee plazas.
Ø The Ministry had mandated fitment of FASTag in M&N categories of motor vehicles with effect from 1st January 2021. Category ‘M’ stands for a motor vehicle with at least four wheels used for carrying passengers. Category ‘N’ stands for a motor vehicle with at least four wheels used for carrying goods, which may also carry persons in addition to goods. In order to further promote fee payment through digital mode, reduce waiting time and fuel consumption, and provide for seamless passage through fee plazas, Government has declared all lanes of the fee plazas on National Highways to be “FASTag lane of the fee plaza” w.e.f. the midnight of 15th/16th February 2021.
Ø More than 7.98 Crore FASTags have been issued till 30.11.2023. The toll collection via FASTag has grown significantly after declaration of all lanes of fee plazas on National Highways as FASTag Lane of the fee plaza w.e.f. midnight of 15th/16th February 2021. Average Daily collection via FASTag on NH fee plaza is Rs. 147.31 Crores and Number of average daily ETC transaction on NH fee plaza is Rs.86.61 Lakhs in F.Y. 23-24 (Till Nov 2023). The constant growth and adoption of FASTag by highway users is very encouraging and has helped increase efficiency in toll operations.
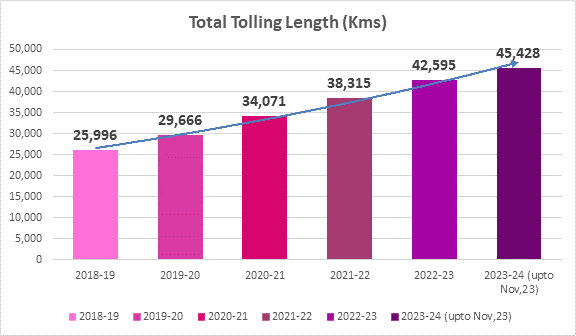
(ii) The Financial Year wise user fee collection on National Highways is as under:
Financial
Year
Total Tolling Length (In Km)
User Fee Revenue
NHAI
MoRT&H
Total amount (In Crore Rupees)
PF (In Cr)
Conc. (In Cr)
Conc. (In Cr)
2018-19
25,996
5,691.42
18,704.78
758.56
25,154.76
2019-20
29,666
6,926.52
19,924.19
786.93
27,637.64
2020-21
34,071
7,875.89
19,283.69
764.22
27,923.8
2021-22
38,315
11,283.94
21,753.15
870.63
33,907.72
2022-23
42,595
16,651.20
30,346.83
1,030.19
48,028.22
2023-24 up to Nov 2023)
45,428
15,862.37
19,782.68
732.74
36,377.79
H. GREEN INITIATIVES
(i) Type Approval of Compressed Gaseous Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles: –
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has inserted new rule 125M in CMVR, 1989 to provide norms for type approval of liquid or compressed gaseous hydrogen internal combustion engine vehicles. It has been prescribed that the safety and procedural requirements for type approval of internal combustion engine vehicles of M and N categories powered by liquid or compressed gaseous hydrogen shall be in accordance with AIS 195:2023, till corresponding BIS specification is notified under the Bureau of Indian Standard Act, 1986 (63 of 1986). Provided that the hydrogen fuel specifications for internal combustion engine vehicles shall be in accordance with IS 16061: 2021.
(ii) Type approval of electric power train vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles: –
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has inserted a new rule 125N in CMVR, 1989 regarding Type approval of electric power train vehicles and hybrid electric vehicle. The definition of Hybrid vehicles is available in various Automotive Industry Standards (AIS); but, till date, a standard definition has not been incorporated in CMVR, 1989. It was, therefore, necessary to incorporate a standard definition of pure electric and hybrid vehicles & its various types, in CMVR 1989. It may also be pertinent to point out that various State governments are providing incentives to electric and hybrid vehicles through their respective state EV policies. Hence, by virtue of the notification it has brought more clarity in the definition and categorization of pure electric and hybrid vehicles.
I. PARVATMALA
1. Convenient and preferred mode of transportation: Ropeways have emerged as a convenient, safe and preferred mode of transportation to provide both, first as well as last mile connectivity to such hilly & inaccessible areas or to help de-congest urban congestion areas. In this backdrop, the Centre is giving a major push to ropeway development in the country. The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRT&H) is responsible for the development of highways and regulating the road transport sector across the country. However, an amendment in the Government of India (Allocation of Business) Rules 1961 in February 2021 allocated the development of ropeways in the country to MoRTH.
2. Varanasi ropeway project of length 3.85 km, is currently under implementation. The ropeway, once operational, will improve convenience for ~1 lac passengers everyday reducing the travel time between the two places from ~45 mins at present to ~16 mins.
3. Planned to Award Projects for 60 Km: Under Parvatmala Pariyojana, ropeway projects of ~60 kms length are planned for award by FY2023-24. Ropeway at Varanasi (Uttar Pradesh) of 3.85 km is under construction. Bids for 9 projects of ~36 km length have been invited like Gaurikund – Kedarnath (Uttarakhand), Govindghat – Ghangaria – Hemkund Sahib (Uttarakhand), Bijli Mahadev (Himachal Pradesh), Dhosi Hill (Haryana), Mahakal Temple in Ujjain (Madhya Pradesh), and Sangam (Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh). Detailed Feasibility Study are underway for additional 05 projects of ~22 km length, such as Kamakhya Temple (Assam), Tawang (Arunachal Pradesh), and Kathgodam – Nainital (Uttarakhand).
J. INDIAN ACADEMY OF HIGHWAY ENGINEERS (IAHE)
Training Programme Conducted during the Year
During the year 2023, the Academy has organized 50 In-campus training program inter- alia includes one 16 weeks foundation training program for Deputy Managers of NHAI; one Orientation course for Ministry’s Senior Technical Officers, Six Mandatory Training Programme on Preparation of DPR for Highway Projects for the personnel of consultants, one course for National Quality Monitors of NRIDA and Eight 15 Days Certificate Courses for Road Safety Auditors. Eight (08) online training programmes on various topics were also organized.
- TOT Model – Under this model, the right of collection of user fee (toll) in respect of selected operational highways constructed through public funding are assigned through a concession agreement as a result of bidding. For a specified period of 15-30 years to the Concessionaire against upfront payment of a lump-sum amount quoted to the Government/NHAI. During the concession period, the responsibility for operations and maintenance of the road assets rests with the Concessionaire. Since its launch in 2018, NHAI has successfully completed 6 rounds of the Road Asset (bundle of roads) of monetization through TOT mode and raised Rs. 26,366 crores. LoAs are issued under ToT bundles 11, 12, 13 & 14 and realization of Rs 15,968 Cr concession fee is expected in FY 2023-24. It is also pertinent to mention here that LoAs for these 4 TOT Bundles were issued by NHAI within one day of opening of the respective Financial bids. Total asset monetization under this model is expected to be Rs 42,334 Cr by the end of FY 2023-24.