Ministry of Finance Year Ender 2024: Department of Financial Services
Ministry of Finance Year Ender 2024: Department of Financial Services
The Department of Financial Services (DFS) continued its momentum of reforms in 2024, building on the robust foundation established through initiatives like the EASE Reform agenda, which emphasises risk assessment, NPA management, financial inclusion, customer service, digital transformation, and more.
The EASE Reforms, governed by the EASE Steering Committee of the Indian Bank’s Association, are now a well-established framework in all Public Sector Banks (PSBs). From EASE 1.0 to the current EASE 7.0, the reforms have brought a transformative shift, focusing on digital customer experience, analytics-driven business strategies, technology-enabled capability building, and enhanced HR operations. The annual EASE Awards event continues to recognise exceptional performances in implementing the reform agenda.
DFS’s strategic interventions have significantly contributed to the reduction of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) in Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs). Gross NPAs have decreased from Rs. 10.36 lakh crore in March 2018 to Rs. 4. 75 lakh crore in March 2024, reflecting the efficacy of measures such as the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), amendments to the SARFAESI Act, and the Prudential Framework for Resolution of Stressed Assets.
In digital payments, the DFS has strengthened its leadership role, driving consistent growth through the DIGIDHAN Mission. Digital payment transactions surged further to an unprecedented 223 lakh crore from January to November 2024, with BHIM-UPI recording over 15,547 crore transactions during the same period, underscoring its role as a key enabler of India’s digital economy.
Financial inclusion remains a top priority, with initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana, MUDRA, Stand Up India, and Atal Pension Yojana making significant progress. As of 2024, these schemes have expanded their reach, ensuring that millions of citizens, especially from marginalized communities, gain access to essential banking, insurance, and pension services.
In the agriculture sector, the DFS has facilitated record credit disbursements, with Agricultural Credit increasing from Rs. 8.45 lakh crore in FY 2014-15 to Rs. 24.30 lakh crore in FY 2023-24. The Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme continues to play a pivotal role, with over 7.92 crore active KCC accounts, providing farmers with timely and hassle-free credit support.
The Department of Financial Services has been instrumental in shaping a resilient and progressive financial landscape in 2024, contributing significantly to India’s economic growth and social well-being.
Following are some of the major achievements & policy initiatives of the Department of Financial Services, Ministry of Finance, in 2024:
PERFORMANCE OF BANKS
As a result of Government’s overarching policy response to recognition of stress, resolution of stressed accounts, recapitalisation and reforms in banks, the financial health and robustness of banking sector has since improved significantly.
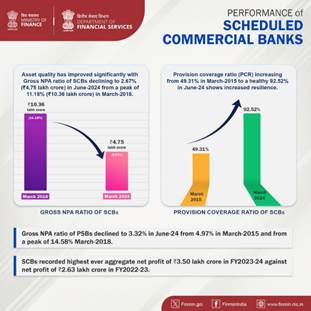
In FY2023-24, PSBs have recorded highest ever aggregate net profit of ₹1.41 lakh crore against net profit of ₹1.05 lakh crore in FY2022-23, and recorded ₹0.40 lakh crore in the first quarter of FY2024-25.
By addressing issues of NPAs and recapitalisation, the reforms contributed to improve the overall credit flow in the economy. PSBs emerged healthier and are poised to facilitate growth in productive sectors of the economy.
DIGITAL PAYMENTS

Key Digital Payment Initiatives at Global Fintech Festival 2024:
UPI:
Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs):
Internet Banking:
Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS) Issuance of Master Direction:
Card-based Payments:
Accessibility to Payment Systems for Persons with Disabilities:
Digitally Enabled Market Cluster:
Introduction of beneficiary account name look-up facility:
Internationalisation Initiatives
UPI achievements during last 3 years:
2021-2022
2022-2023
2023-2034
Staff Welfare Fund
Staff welfare fund (SWF) is a fund allocated by the PSBs for the welfare-related activities (health-related expenses, subsidies on canteen, sports and cultural activities, education-related financial assistance etc.) in respect of working and retired officials of PSBs. SWF was given a fillip by increasing the maximum ceiling of annual spending. The ceiling, last revised in 2012, was thoroughly revised after taking into consideration the number of employees and retirees in PSBs as of 2024 and the change in the business mix of the PSBs. PSBs were categorized into four different slabs based on their business mix and the employee strength and the ceilings were revised accordingly. Post revision, the combined maximum annual expenditure ceiling of SWF for all the 12 PSBs has increased from Rs.540 crore to Rs.845 crore. This increase will benefit 15 lakh staff including the retired employees of all the 12 PSBs.
Creation / Increase of Chief General Manager Posts In Nationalised Banks

Union Finance Minister has approved the creation of Chief General Manager (CGM) posts in five additional nationalized banks: Bank of Maharashtra, Central Bank of India, Indian Overseas Bank, Punjab & Sind Bank, and UCO Bank. Previously, CGM posts existed in only six out of eleven nationalized banks. This decision will increase the number of CGM posts, enhancing the administrative and functional structure within the banks. CGM posts serve as a critical link between General Managers (GMs) and Executive Directors, improving oversight and supervision in areas like digitalization, cybersecurity, and financial inclusion.
The number of CGM posts will now be based on a ratio of one CGM for every four GMs. This expansion will also benefit Deputy General Managers (DGMs) and Assistant General Managers (AGMs). With this change, the total CGM posts across the eleven banks will rise from 80 to 144, GM posts from 440 to 576, DGM posts from 1320 to 1728, and AGM posts from 3960 to 5184. This move addresses demands from banks and supports their growth in business and branch expansions.
Financial Inclusion Schemes
1. Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)

Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) was launched as the National Mission for Financial Inclusion on 28.8.2014. It aimed to ensure comprehensive financial inclusion of all households in the country by providing universal access to banking facilities with at least one basic bank account to every household, financial literacy, and social security cover.
The scheme offers:
Progress under PMJDY (as on 20.11.2024):

The Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) is a one-year personal accident insurance scheme, renewable from year to year, offering coverage for death/disability due to an accident and is available to people in the age group of 18 to 70 years having a bank account who give their consent to join and enable auto-debit
Progress under PMSBY (as on 20.11.2024):

The Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY) is a one-year life insurance scheme, renewable from year to year, offering coverage of Rs. Two lacs for death due to any reason and is available to people in the age group of 18 to 50 years having a bank account.
Progress under PMJJBY (as on 20.11.2024):

The Prime Minister launched Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY) on 08.04.2015 with an objective of providing access to institutional collateral free credit to micro enterprises up to Rs.10 lakh.
Features:
Progress under MUDRA (as on 01.11.2024 since launch of scheme)

Progress under Stand-Up India (as on 30.11.2024 since launch of scheme)
6. Atal Pension Yojana

Progress under APY during last 8 years
31.3.17
31.3.18
31.3.19
31.3.20
31.3.21
31.3.22
31.3.23
31.3.2024
Subscribers
enrolled
(cumulative
Fig .in lakh)
48.83
97.05
154.18
223.01
302.15
401.27
520.58
643.52
NPS-Vatsalya

Bima Sakhi Yojana launched
The Prime Minister launched the Bima Sakhi Yojana from Panipat on 9th December 2024. The ‘Bima Sakhi Yojana’ initiative of Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) is designed to empower women aged 18-70 years, who are Class X pass. It is a Stipendiary Scheme, exclusively for Women , with a stipendiary period of 3 years. Bima Sakhis will receive specialized training and a stipend for the first three years to promote financial literacy and insurance awareness. After training, they can serve as LIC agents and the graduate Bima Sakhis would have the opportunity to qualify for being considered for Development Officer roles in LIC.
Ground Level Agriculture Credit (GLC)
(In Rs. Crore)
FY
Overall GLC Target
Overall GLC Achievement
Target for Allied Activities
Achievement for Allied Activities
2019-20
13,50,000
13,92,729
–
–
2020-21
15,00,000
15,75,398
–
–
2021-22
16,50,000
18,63,363
61,650
1,29,453
2022-23
18,50,000
21,55,163
1,26,000
2,61,538
2023-24
20,00,000
25,48,635
2,93,000
2,81,323
2024-25*
27,50,000
10,56,942
4,20,000
1,38,106
*Data for FY 2024-25 is provisional as on 30.09.2024
Kisan Credit Card (KCC)

(No of Operative KCCs in actuals & Amount outstanding in Rs. Crore)
As on date
No. of Operative Accounts
Amount Outstanding
31.03.2020
6,52,80,254
7,43,573
31.03.2021
7,37,45,010
7,53,431
31.03.2022
7,14,90,107
8,15,314
31.03.2023
7,34,70,282
8,85,464
31.03.2024
7,75,04,234
9,81,763
30.09.2024(current FY)
7.72 crore
9.99 lakh crore
- As per RBI’s provisional data: