Ministry of Coal’s Year End Review-2024
Ministry of Coal’s Year End Review-2024
1. COAL PRODUCTION/SUPPLY
1.1. Coal Production
1.2. Coal Supplies
· During Calendar Year 2024 (upto 15th December, 2024), the country has supplied about 963.11 MT(Provisional) of coal as compared to about 904.61 MT (Provisional) coal during the same period of last year with a growth of about 6.47%.
· During Calendar Year 2024 (upto 15th December, 2024), the coal supply to Power Sector was 792.958 MT(Provisional) as compared to 755.029 MT (Provisional) coal during the same period of last year with a growth of 5.02%.
· During Calendar Year 2024 (upto 15th December, 2024), the coal supply to Non-Regulated Sector (NRS) was 171.236 MT(Provisional) as compared to 149.573 MT (Provisional) during the same period of last year with a growth of 14.48%.
1.3. Mission Coking Coal
With transformative measures taken by Ministry of Coal under ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’, domestic raw Coking Coal production is likely to reach 140 MT by 2030. The total domestic raw coking coal production during the financial year 2023-24 is 66.821 million tonnes (MT). The domestic raw coking coal production target for the financial year 2024-25 is 77 MT.
Ministry of Coal has taken following steps to reduce these imports:-
1.4. Setting up of New Coking Coal Washeries
Three new coking coal washeries with a capacity of 11.6 MTY have been already commissioned. Additionally, new coking coal washeries by BCCL (03 nos. with cumulative capacity of 07 MTY) and CCL (05 nos. with cumulative capacity of 14.5 MTY) are planned. Status of 08 Coking Coal Washeries-
2. REFORMS & POLICY
2.1. Coal Linkage Policy implementation
During Calendar Year 2024 (up to 2nd December, 2024) one tranche (VIIth) held under the NRS e-auction in which 17.84 MT was booked against the total offered quantity of 34.65 MT.
· Four tranches under SHAKTI B(VIII-A), was conducted by Coal India Limited for coal Linkage Auction from January to September 2024. Out of total offered quantity of 47.64 MT of coal, 23.98 MT of coal have been booked by successful bidders.
2.2. Modification in Price Notification for coal by making the ROM price of Regulated Sector applicable to the Gasification Projects
As part of the initiative, under the Non-Regulated Sector (NRS) linkage auction policy dated 15.02.2016 of Ministry of Coal, a new sub-sector of ‘Production of Syn-Gas leading to coal gasification’ was created on 14.02.2022. The gasification project proponents are required to participate under the linkage auctions in this sub-sector to avail a coal linkage. NRS linkage auction policy states that the initial floor price shall be set at the relevant CIL / SCCL ROM price and the bidders shall bid for premium above this price.
The floor price for the linkage auctions for NRS is not fixed by Ministry of Coal and is decided by CIL / SCCL in terms of the linkage auction policy dated 15.02.2016. The floor price is dependent on the price notification of coal issued by CIL / SCCL.
Considering the clean coal initiatives, including ‘Coal Gasification Mission’ of Ministry of Coal as well as the views of NITI Aayog to recognize the critical significance of source and price of coal, the floor price of the linkage auctions for the sub-sector ‘Production of Syn-Gas leading to coal gasification’ may be considered by CIL / SCCL to be the ROM price of the Regulated Sector. Accordingly, on 16.12.2024, CIL /SCCL have been directed to undertake the following:
2.3. Launch of Mine Closure Portal
Coal mine closure is a crucial issue in India due to the significant environmental and socio-economic impacts coal mining has on communities and ecosystems. India, one of the largest coal producers in the world, has increasingly recognized the need for sustainable mine closure practices, driven by environmental concerns, the depletion of coal reserves, and the country’s transition toward cleaner energy. Brief background is as under-
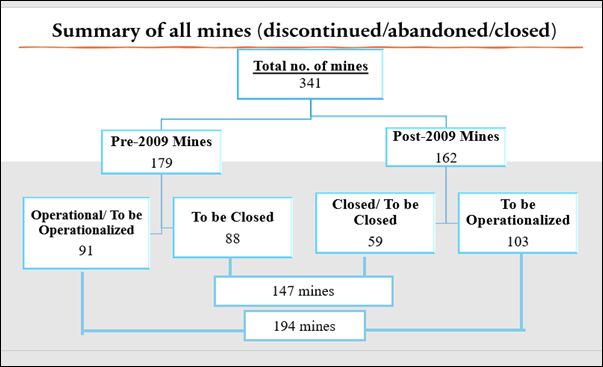
Coal mine closure in India is governed by the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 and Coal Mine Regulations, 2017. Additionally, Ministry of Coal has issued the Mining Plan Guidelines 2020, wherein Mine closure is the integral part of mining Plan. Ministry of Coal issued 1st Mine Closure guidelines in 2009. These guidelines were further revised in the years 2013 and 2020. As per the 2020 guidelines, the closure cost of Rupees Nine Lakh per hectare in case of opencast and Rupees one lakh fifty thousand per hectare for underground Mine based on base year i.e. 01.04.2019 were estimated. Mines closed before 2009 often lacked a structured closure framework, leading to non-scientific closures. Acknowledging the physical hazards and environmental consequences associated with these abandoned mines, the Ministry issued guidelines in October 2022 for managing mines closed before 2009, categorizing them as discontinued, abandoned or closed.
· Environmental Rehabilitation: The closure plan emphasizes restoring the mined land by filling open pits, stabilizing slopes, managing waste dumps, and planting vegetation. Afforestation is a major part of environmental rehabilitation to restore ecosystems disturbed by mining.
· Water Management: Water bodies impacted by mining operations are rehabilitated to ensure that they do not suffer from contamination due to coal mining waste or acid mine drainage. Proper drainage systems are installed to prevent waterlogging or groundwater contamination.
· Waste Management: Handling mine waste, including overburden is essential to prevent environmental hazards. Proper management ensures that hazardous materials do not continue to impact the environment post-closure.
· Land Reclamation: Coal mine areas are typically rehabilitated for agricultural use, afforestation or for community use, depending on local needs and conditions.
In terms of statistics, a total of 179 pre-2009 and 162 post-2009 mines, considered abandoned/discontinued have been identified in Coal Companies. Of these, 147 mines are identified for closure and remaining abandoned/discontinued mines are either merged with existing for re-operationalization.
Union Minister for Coal & Mines, launched the ‘Mine Closure Portal,’ during CIL’s 50th Foundation Day celebrations held in Kolkata. The portal, developed by CMPDI, CIL, will help monitor mine closure activities, timelines and expenditures associated with these processes. This portal will encompass mine closure activities across India’s coal sector including both public sector undertakings (PSUs) and private companies. The Ministry of Coal and the Coal Controller’s Organisation (CCO) are also key stakeholders of this portal.
2.4. Launch of National Coal Mines Safety Report Portal
Coal mining in India was primarily being carried out by Central and State PSUs and also by other PSUs and private companies for captive use. However, now it is open for commercial mining also. Further, Power Generation Companies have started coal mining in recent past to ensure guaranteed supply of coal to captive power plants by having mining leases. Similarly, coal mines have been allocated to captive users in iron and steel industries as well.
Outsourcing of operations through different modes like MDOs are the most preferred way of doing business today, including PSUs. Larger participation of MDOs, Contractors and Service Providers is most expected scenario in mining today. Ministry of Coal, as the operating Ministry has the onus to maintain consistency in policy and implementation strategy to make Indian coal mines of high safety standard.
In this regard, Ministry of Coal formed a High-Level Expert Committee (HLEC) on Safety comprising experts from various fields on 01.01.2021. As per the short-term recommendations of the committee, “Action Taken Report (ATR) on all DGMS enquiry should be uploaded by the respective Mine operators on their website. Expert committee can study these ATRs and submit its recommendations/advise to MoC accordingly.” Subsequently, a web portal for uploading of data by the coal companies related to safety was notified by MoC on 1st Feb’22 which was launched by Minister of Coal on 13th April’22. Further on recommendations of HLEC, Ministry of Coal issued Safety and Health Management Guidelines in December, 2023. A module regarding the same is now added in portal and portal has been revamped various other features.
Therefore, Minister of Coal and Mines launched the National Coal Mines Safety Report Portal on 17.12.2024 at the 49th Standing Committee on Safety in Coal Mines.
The National Coal Mines Safety Report Portal, developed by Ministry of Coal, under the guidance of the High-Level Expert Committee on Safety in Coal Mines, represents a significant advancement in coal mine safety management. The portal monitors actions based on recommendations from various inquiries, aiming to reduce accidents and improve safety practices across the industry.
It features two key modules: the Accident Module, which facilitates near- real time reporting and management of incidents and the Safety Audit Module, which strengthens safety protocols.
Objective of the portal:
The portal supports the Ministry of Coal’s commitment to a “Culture of Mine Safety” by leveraging technology and risk assessment to enhance safety, productivity and employee well-being in the coal mining sector.
2.5. Land Acquisition
The land acquired u/s 9(1) and vested u/s 11 of the Coal Bearing Areas (Acquisition and Development) Act, 1957 for subsidiaries of Coal India Limited
“During the period from 01.01.2024 to 18.12.2024, a total of 16838.34 acres of land have been acquired under section 9 (1) of the Coal Bearing Areas (Acquisition and Development) Act, 1957 for subsidiaries of Coal India Limited. A total of 17371.03 acres of land have been vested to subsidiaries of CIL under section 11 (1) of the CBA (A&D) Act, 1957”
Details of land acquired by various subsidiaries of Coal India Limited under various Acts (i.e., CBA Act, RFCTLARR, Act (erstwhile LA Act, 1894) and through agreement, etc., which is uploaded on PM Gatishakti Portal as on 18.12.2024, are given below: –
Sl. No.
Name of Subsidiary
Total Land Acquired (Ha.)
Land data uploaded on PM
GatiShakti Portal
1.
ECL
26,949
25144.68
2.
BCCL
16,381.09
16381.09
3.
CCL
63,232
63,232
4.
WCL
39,277.15
39,277.15
5.
NCL
25,697.94
24,294.60
6.
SECL
57,571.70
57,571.70
7.
MCL
31,910.764
31,910.764
TOTAL
2,61,019.644
2,57,811.984
2.6. Increase in area limits u/s 6(1) of MM(DR) Act, 1957
Vide Order dated 07.03.2024, the area limits under Section 6(1) of the Mines and Mineral (Development & Regulation) Act, 1957 for grant of Prospecting License / Mining Lease have been increased. Details are as under:
Sl. No.
State
PL limit
ML Limit
1
Maharashtra
40
40
2
Odisha
45
45
3
West Bengal
no change
25
4
Madhya Pradesh
35
35
5
Jharkhand
75
75
6
Chhattisgarh
90
90
2.7. Amendment in Land Use Policy of Central Public Sector Undertaking in Coal Sector
Land Use Policy of Central Public Sector Undertaking has been amended on 29.07.2024 to provide for leasing of mining and/or surface right in such overlapping lands already acquired and vested in the Government Companies under various acts to coal block allottees and for extending the policy dated 22.04.2022 to lands already purchased/acquired under various acts.
2.8 Amendment in timeline in CIMS Portal
After stakeholder consultations on functioning of CIMS portal and other related issues, an amendment was affected in the timeline of registration in CIMS portal. The importer can apply for registration not earlier than 60th day and till the arrival date (Zeroth Day) of consignment. The Automatic Registration Number shall remain valid for a period of 75 days. Importer shall have to enter the Registration Number and expiry date of Registration in the Bill of Entry to enable Customs for clearance of consignment.
2.9. Coal Mines Provident Fund Organisation (CMPFO)
3. INFRASTRUCTURE PROJECTS
3.1. First Mile Connectivity [FMC]
Ministry of Coal takes up 102 First Mile connectivity Projects having capacity 1040 MT for seamless evacuation of coal. Out of this, 39 Projects (37-CIL & 2-SCCL) of 386 MTPA capacity have been commissioned.
To strengthen India’s energy security and to realize Atmanirbhar Bharat by replacing imported coal with domestically mined coal, Ministry of Coal has set a target to produce 1.31BT in FY25 and 1.5BT in FY30. Development of coal transportation that is cost efficient, fast and eco-friendly manner is important goal of the country.
Keeping in view the increase in coal evacuation in future, Ministry of Coal is working on the development of National Coal Logistic Plan including First Mile Connectivity through railway sidings near coal mines and strengthening of Rail Network in Coalfields.
MOC has formulated a strategy to develop an integrated approach for eliminating road transportation of coal in mines and has taken steps to upgrade the mechanized coal transportation and loading system under ‘First Mile Connectivity’ projects. Coal Handling Plants (CHPs) and SILOs with Rapid Loading Systems will have benefits like crushing, sizing of coal and speedy computer aided loading.
MOC has undertaken 102 first mile connectivity (FMC) projects (94 – CIL, 5- SCCL & 3 – NLCIL) of 1040 MTPA capacity, out of which 39 Projects (37-CIL & 2-SCCL) of 386 MTPA capacity have been commissioned. Remaining projects are to be implemented by FY 2027-28.
With reduced manual intervention, precise pre-weighed quantity and better quality of coal can be loaded. Improved loading time will bring down the wagon idling increasing their availability. Easing the load on road networks promotes cleaner environment and savings on diesel. It will be an all-round win-win situation for the company, railways and the consumers.
3.2. Initiatives under PM Gati Shakti
Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti National Master Plan (PMGS-NMP) was launched on 13th October 2021 to ensure integrated planning and coordinated execution of infrastructure projects. Project reports of Coal India Limited (CIL) are analyzed based on available information on PMGS-NMP portal for integrated planning to boost Coal production.
The Ministry of Coal, in view of cleaner environment in coal transportation has given momentum in rail evacuation and also initiating news efforts to gradually move away from road movement of coal in country. MoC has mapped more than 100 layers and mapped on portal along with attributes and metadata. These layers will speed up the process of Planning by consideration of all requirements related to Ministries during the planning and execution stage in projects.
3.3. Integrated Coal Logistic Plan and policy
National Logistics Policy was launched by Prime Minister in September, 2022 with an objective to enhance logistics efficiency, reduce logistics cost and to improve the logistics performance of the country to be among top 25 nations of the world.
The Ministry of Coal has set a goal to produce 1.3 billion tonne of domestic coal by FY 2027 and 1.5 3 billion tonne by FY 2030 to advance Atma-Nirbhar Bharat and increase India’s energy security by substituting imported coal with locally mined coal. In view of projected coal demand, the existing evacuation infrastructure may not be adequate to optimally evacuate the projected coal demand and can pose a challenge. It was imperative to re-evaluate the existing logistics infrastructure available across all transportation modes of coal evacuation in an integrated manner and to plan for sustainable development of future infrastructure that leverages the strengths of different modes leading to optimized total logistics cost of coal movement at the National Level.
Accordingly, an extensive exercise has been undertaken for Origin-Destination study for freight movement of coal, based on the scientific data, congestion analysis was carried out and identification of railway infrastructural gaps for all the blocks currently in operation and also proposed to be operationalized for the peak production requirement of the country.
This exercise has been undertaken in close consultation with stakeholders Ministry of Steel, Ministry of Power, Ministry of Railways, Ministry of Road and Transport and Highways, Ministry of ports Shipping and Waterways, Niti Aayog and DPIIT. Based on this extensive exercise, M/o Railways & M/o Coal have jointly identified 38 critical infrastructure gap projects. Such projects have been incorporated in the Coal Logistics Action Plan.
Logistics Policy and Plan with a vision to develop technologically enabled, integrated, cost effective, resilient, sustainable and trusted logistics ecosystem for coal evacuation. This strategic framework aims to propel accelerated demand and supply of coal sector in FY2030. Coal Logistics Policy and Integrated Coal Action Plan was launched on 29.2.2024.
Outcome of this Integrated Coal Logistics Plan and policy will be as under-
Impact of the Integrated Coal Logistics Plan and policy will be as under –
4. COAL BLOCK ALLOCATION
4.1. Commercial Mining
To reduce import of coal and to promote domestic production, auction-based regime introduced in 2014 allowed private sector participation, however, it was limited to captive usage in own end use plants. The sector has been opened up for commercial coal mining by private players in 2020 and first ever successful auction of commercial mining was launched by the Prime Minister on 18.06.2020 and concluded with allocation of 20 coal mines
4.2. Coal Production from Captive/Commercial coal blocks
Coal production from Captive/ Commercial mines for the period between Jan 2024 to Nov 2024 is 162.1 MT.
5. ASSET MONETIZATION
In the year 2023-24 against the NITI Aayog Target of Rs.50118 crore, the Ministry of Coal achieved Rs.56794.49 crore.
Status of Asset Monetization in FY 2024-25 till November 2024 against NITI Aayog Target of Rs.54722 crore is as follows:
S. No
Assets Category
Amount in crores
1
Coal Block Auction
19,156.43
2
MDO
2,765.43
3
Abandoned Mines
490
Total
22,411.86
Ministry of Coal achieved Capex Target for the FY 2023-24 of Rs.29449.08 cr which is 140.03% of the annual capex target. Detail of Capex Achieved in FY 2023-24 and in FY 2024-25 till November 2024 is given below:
Amount in crores
Particulars
CIL
NLCIL
SCCL
Total
FY 2023-24
MoU Target for 2023-24
16500
2880
1650
21,030
Achievement
23475
4270
1704.08
29449.08
% achievement
142.27%
148.26%
103.28%
140.03%
FY 2024-25
MoU Target for 2024-25
15500
2429
1,600
19529
Achievement till Nov 24
9023.07
4039.17
980.66
14042.9
% achievement till Nov 24
58.21%
166.29%
61.29%
71.91%
6. CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
6.1. CSR Expenditure
CIL booked a CSR expenditure of Rs.637.89 cr. [FY 23-24 (Jan. to Mar. 2024 (FY 23-24) – Rs. 275.66 cr. + Rs. 362.23 cr. for Apr. – Nov. 2024 (FY 24-25)] on a consolidated basis during 2024 (January – November) which is 14% higher than the figure for similar period in 2023 which stood at Rs.561.14 cr.
Major projects taken up during the year
6.2 Mission Mode Recruitment
Total 13341 appointment letters for various posts (CIL-9384 & NLCIL- 3957) were issued under Mission Mode Recruitment up-to December 2024.
7. SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
7.1. Greening Initiatives: Bio-Reclamation/Plantation

Launch of VA – 2024 by Minister of Coal & Mines

Drone view of Vriksharopan Abhiyan – 2024 at SECL

Launch of Report on Greening Initiative in Coal & Lignite PSUs

Reclamation against time scale in Jayant OCP, NCL
7.2. Development of Eco-Parks on Reclaimed Land & Mine Tourism

Chandra Shekhar Azad Eco-park, Bina Project, NCL

Nigahi Eco Park, near Bareja Pond, NCL

Eco-Park developed at Gautham Khani OC by SCCL
7.3. Utilization of Mine water for Community Use
· Mine water is crucial for diverse community needs such as domestic use, irrigation, groundwater recharge and industrial applications.
· During January, 2024 to November, 2024, 3,623 LKL volume of treated mine water has been offered for community purposes of which 1,296 LKL for drinking purpose and 2,327 LKL for irrigation purposes.
· During last 5 Years till March, 2024, volume of mine water supplied for community purposes has been around 18,513 LKL which is anticipated to benefit around 18.63 lakh population in 1,055 villages of coal bearing States. Volume of mine water supplied for irrigation purpose has been 7,010 LKL & for domestic/ drinking purposes has been 11,503 LKL.
· For the next five years, from 2024-25 to FY 2028-29, Coal/Lignite PSUs is committed to offer 20,000 LKL of mine water for community use.

Post- Mining void at Piparwar OCP, CCL for Mine water Utilization

Farming on OB dump at JKKC Eco-restoration site in Kusunda area of BCCL
· Recognizing the critical role of water bodies in maintaining ecological balance, Minister of Coal and Mines, Shri G Kishan Reddy, has released comprehensive guidelines for the rejuvenation of traditional water bodies in coal and lignite mining regions. This initiative aligns with the guidelines of Mission Amrit Sarovar (2022) from the Department of Rural Development, Government of India, and will serve as a CSR initiative by Coal/Lignite CPSUs, including Coal India Limited (CIL) and NLC India Limited (NLCIL). The project aims to rejuvenate and establish at least 500 water bodies in and around coal and lignite mining areas over the next five years (FY 2024-25 to FY 2028-29). CPSUs will manage water bodies within leasehold areas, while District Collectors will handle the water bodies outside the leasehold area. Each new water body will have a pondage area of at least 0.4 hectares and a capacity of around 10,000 cubic meters. Additionally, the project will leverage mine water from active and abandoned mines, aligning with the Government of India’s Jal Shakti Abhiyan.
7.4. Alternative Usage of Overburden (OB)
· To promote Circular Economy (Waste to Wealth in Coal Sector), a total of 4 OB Processing Plants and 5 OB to M-sand Plants have been commissioned so far by Coal/Lignite PSUs.
· 6 more such plants are under various stages of development.

Processed Overburden Plant at Gonegaom Area by WCL & at Srirampur OC Mines by SCCL

Overburden to M-Sand Plant at Amlohri Plant, NCL
7.5. Energy Efficiency Measures

E-Vehicle at CIL Corporate HQ, Kolkata

Pump House with IE3 Motor at SECL
8. OTHER ACTIVITIES
8.1. Awards for Star Rating of Coal & Lignite Mines
Ministry of Coal organized prestigious Star Rating Awards ceremony on 21st October 2024, to recognize the exceptional performance of Coal and Lignite mines. For the base year 2022-23, total 43 mines (10 underground mines and 33 opencast mines) awarded 5 Star Rating.
With a steadfast commitment to elevating industry standards, the Ministry has implemented a well-defined mechanism to enhance performance across key criteria, promoting responsible coal mining practices for sustained growth and development. The Minister of Coal and Mines, Shri G. Kishan Reddy graced the occasion as the chief guest.
Ministry of Coal is committed to sustainability of Coal and Lignite mining, enhancing overall performance of coal mines in the country by championing sustainable mining practices and fostering competitiveness among mines. Therefore, the Ministry has formulated Star Rating Policy to distinguish outstanding performance of coal mines and accord them the recognition.
The Star rating policy outlines Star Rating criteria across seven comprehensive modules: “Mining Operations, Environmental factors, Adoption of Technologies-Best Mining Practices, Economic Performance, Rehabilitation & Resettlement, Worker related Compliance, and Safety & Security.” A total of 50 evaluation parameters in opencast mines and 47 evaluation parameters in underground mines are specified in these seven modules. The Star Ratings are awarded on a scale from Five Star to No Star, evaluating each mine’s achievements holistically.
Further, Ministry of Coal has formed a committee under the chairmanship of Additional Secretary to review the parameters of Star Rating as per the present scenario of the coal sector and further recommend the similar evaluation in line with the mines used in other countries.
8.2. S&T Achievement
Government has given high thrust on Research & Development (R&D) in coal technologies for improvement in existing uses and also in futuristic fields for diversification for long term sustainable growth.
A Centre of Excellence on Research & Development i.e. “National Centre for Coal & Energy Sector” (NaCCER) was inaugurated by Minister of Coal on 7th October’2024 at CMPDI, Ranchi.


8.3. Special Campaign for disposal of pendencies 4.0
In line with Government of India’s vision for enhancing operational efficiency, the Ministry of Coal conducted Special Campaign 4.0 comprising a Preparatory Phase (14-30th September 2024) & Implementation Phase (2-31st October 2024). The Ministry of Coal along with its Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs), attached offices, and autonomous organizations, participated in the campaign with enthusiasm and achieved outstanding results. Key activities included rapid reviews and weeding of both physical and electronic files. Special attention was given in reducing the pendency in the number of references from Members of Parliament, VIP references, Public Grievances and PMO.
Ministry of Coal secured 1st position in Space Freed (78.46 lakhs Sq. Feet), and 4th position in Revenue Generation (Rs.38.27 crores) from Scrap Disposal, amongst all the Ministries/Departments, showcasing MoC’s proactive efforts in resource optimization and sustainability.
The achievements of the Ministry during the Special Campaign 4.0 are as under:

The Swachhata initiatives led to the clearance of large areas within office campuses and adjoining areas, creating more usable space. This effort not only contributed to a cleaner environment but also generated a large amount of revenue through the disposal of scrap material.
The Ministry of Coal’s efforts resulted in a remarkable improvement in office cleanliness, with before-and-after photographs of cleaning sites clearly showing substantial progress.

BEFORE AFTER
Office Space made by clearing Scrap at CMPDI, Dhanbad, Jharkhand


BEFORE AFTER
Amrit Pharmacy made by clearing Scrap at Indira Vihar Hospital, Bilaspur by South Eastern Coalfields Limited (SECL)


BEFORE AFTER
BCCL converted an unused area into a table tennis court, fostering employee well-being and work-life balance.
Special Initiatives: Citizen Involvement and Community Outreach
The campaign’s reach extended to all corners of the country, including remote and rural areas. In addition to internal cleaning and record-keeping efforts, the Ministry extended the campaign’s reach to the community through a series of public engagement programs Swachhata Rallies, Nukkad Nataks, and Samadhan Camp-1 were organized to engage citizens and raise awareness about the importance of cleanliness, especially school children—were encouraged and sensitized about campaign. Welfare initiatives for Safai Mitras, including health check-ups and recognitions, were also organized to recognise their vital role in sustaining cleanliness.

As part of Special Campaign 4.0, a workshop on Records Management was conducted in collaboration with the National Archives of India, where Ministry officials received training on effective record management practices, enhancing data accessibility and organizational efficiency. Additionally, a “Cyber Jagrookta” workshop was held to raise awareness among officials about cybersecurity and to sensitize PSUs and organizations under its administrative control about current cyber security challenges. The workshop focused on equipping participants with best practices to enhance their cyber defences, understand security threats, and apply practical solutions to real-world scenarios Various activities, including clean desk competitions, quizzes, and a “Waste to Wonder” contest, were also organized to promote engagement and innovation in maintaining clean and efficient workspaces.
Adding a creative dimension to the Special Campaign 4.0 some of the Organizations of Ministry of Coal with enthusiastic workforce participation have undertaken the following initiatives with citizen involvement and collective action as part of good practice that will support future initiatives.
Cleaning of Water Resources

Cleaning at Godavari Ghat at Ramagundam – I Area of SCCL located in Peddapelli District of Telangana State by Singareni Collieries Company Limited (SCCL)
Scrap Disposal: Herbal Park at Scrap Site

NLC India Ltd. cleared scrap yard -2,30,000 sq. ft. at Mine-I and planted over 40 varieties of herbal plants at Pothigai Herbal Park at Neyveli Township, Cuddalore Dist, Tamil Nadu.
Solar:

Roof Top Solar Panel installed on DIG Complex,Steel Gate,Koyla Nagar, Dhanbad, Jharkhand
AI- Bin

CIL installed two Smart-Re bins for effective waste segregation and plastic bottle disposal, promoting social inclusion, user-friendly design, and cost-efficiency.
Waste to Art


CMPDIL created a “Golden Deer and Fawn” sculpture from waste materials, combining artistry with sustainability. Additionally, a 7-foot sculpture of Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose was crafted from scrap at BCCL, Dhanbad
Solar

CMPDIL installed 3 x 5 KW Solar Trees at its campus & BCCL installed 2.3 MW Roof top Solar panels on office & residential buildings, inaugurated by MoS Shri Satish Chandra Dubey, advancing clean renewable energy and sustainability
Inventory Management Portal
Ministry of Coal digitized its inventory management for efficient tracking and distribution of goods, enhancing accountability and reducing manual errors.
The achievements under Special Campaign 4.0 underscore the Ministry of Coal’s commitment to sustainability, efficiency, and employee well-being. From innovative waste management solutions and renewable energy, initiatives to creative use of scrap materials and optimized record keeping, these efforts have transformed workplaces and strengthened organizational practices. As the campaign concludes, the Ministry remains dedicated to maintaining these improvements and fostering a cleaner, more efficient work environment that aligns with the Government’s vision for Swachhata and operational excellence.
8.4. IT/Media Initiatives
The Ministry of Coal has made significant strides in standardizing and enhancing the IT working environment and service delivery through the implementation of various e-Governance initiatives. These include the Single Window Clearance System, Coal Import Monitoring System (CIMS), Coal Projects Monitoring Portal, and the Star Rating of Coal Mines. Additionally, the Ministry is actively facilitating Cyber Audits to ensure a secure digital ecosystem.
Recognizing the importance of Cyber Security, the Ministry of Coal and its PSUs have been taking regular and proactive measures to strengthen their defences. These efforts include the nomination of Chief Information Security Officers (CISO), the preparation of Cyber Crisis Management Plans (CCMP), and strict adherence to security guidelines. Regular training sessions are conducted to educate employees about cyber threats such as phishing and malware. Furthermore, Cyber Security Audits are regularly conducted to assess and improve the effectiveness of implemented measures.
To raise awareness on Cyber Hygiene, information is being disseminated through social media platforms and banners/standees placed across the Ministry and PSUs, ensuring maximum outreach and sensitization.
The Ministry of Coal has made significant strides in its media outreach to engage the public effectively. Through regular press releases, the Ministry has successfully communicated key initiatives, policies, and achievements. Additionally, the Ministry has collaborated with other Government Ministries such as the Ministry of Health, Ministry of Tourism, and Ministry of Education etc. to amplify its reach and visibility. This unified approach has led to increased exposure and highlighted the Ministry’s collaborative efforts.
The Ministry of Coal maintains an active presence across multiple social media platforms, including X (Twitter), Facebook, Instagram, Threads, and LinkedIn, offering real-time updates to encourage engagement and promote transparency. Furthermore, the Ministry contributes to public discourse by publishing articles in leading newspapers and magazines, providing valuable insights into the coal sector’s development and sustainability efforts. This comprehensive media strategy highlights the Ministry’s commitment to effective communication and public awareness.
9. FUTURISTIC AGENDA
Diversification has become a strategic necessity for CPSEs in the coal industry. The traditional reliance on coal is increasingly seen as unsustainable, both environmentally and economically. Diversification efforts are aimed at reducing dependence on coal, enhancing sustainability, and ensuring long-term viability. CPSEs are exploring various avenues, including renewable energy projects, coal gasification, and advanced technologies such as pump storage plants. These initiatives are designed to align with global trends, meet regulatory requirements, and tap into new revenue streams.
Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) in the coal industry have recognized the need to diversify their operations to adapt to changing market dynamics and address environmental concerns. These enterprises have adopted various strategies to mitigate the risks associated with dependence on coal and position themselves for sustainable growth.
9.1. Coal Gasification Project
Coal gasification is the process of producing syngas—a mixture consisting primarily of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and water vapour (H2O)—from coal using controlled heat in a low-oxygen environment. As of 01.04.2024, India’s estimated coal reserves stand at approx. 389 BT. Coal gasification offers a pathway for diversifying coal use in a more sustainable manner. It is more efficient and environmentally friendly, producing lower emissions compared to traditional combustion methods. Syngas, produced through coal gasification, can be utilized for the production of gaseous and liquid fuels, chemical, petrochemicals as well as power generation. Under the Coal gasification Mission, Ministry of Coal (MoC) set an ambitious target to achieve 100 MT of coal gasification by 2030, to fulfil India’s dual objective of self-reliance and energy independence.
A. Progress on Scheme:
· Scheme for Financial Incentive of Rs.8500 cr. to coal gasification projects approved by CCEA on 24.01.2024. Guidelines for implementing the Scheme issued on 07.02.2024.
· RFP for all the 3 categories of financial assistance scheme published on 15.05.2024. List of coal mines with long-term linkage, offered by CIL for coal gasification projects have also been published on 25.06.2024.
· 03 applicants under Category-I and 01 applicants under Category-III have been declared successful. LoA has been issued to them. The timelines for opening of bid for Category-II RFP is January 10, 2025.
· CIL /SCCL have been directed modify their Price Notification for coal by making the ROM price of Regulated Sector applicable to the Gasification Projects as well, for the coal gasification projects commissioning within a period of 7 years.
· On 24.01.2024, the CCEA approved CIL’s equity investment exceeding 50% limit in its joint ventures with GAIL and BHEL for setting up coal gasification projects.
B. Underground Coal Gasification:
India’s first pilot project for underground coal gasification initiated and drilling has commenced at the Kasta block on 22.06.2024.
C. Status of the Projects:
Category-I Projects
After technical and financial evaluation, the following projects have been selected for receiving financial incentive as on 02.12.2024:
· Project 1: CIL-BHEL JV (Coal to Ammonium Nitrate) – CIL and BHEL incorporated the JV namely Bharat Coal Gasification & Chemicals Limited (BCGCL) on 21.05.2024. Tenders for LSTK contracts have been issued. Land of 350 acres in Jharsuguda, Vasundhara coal mine has been identified. Topographical survey and geotechnical survey completed. TOR uploaded on Parivesh portal – MoEF&CC on 23.07.2024. Tenders for LSTK contracts have been issued. Responses to pre-queries published.
· Project 2: CIL-GAIL JV (Coal to SNG) – JV Agreement between CIL and GAIL executed on 05.08.2024. PMC work awarded to PDIL. Land is to be identified. Sonepur Bazari coal mine has been linked to the project. EOI for pre-qualification of licensors of coal gasification technology published on 12.09.2024. Bid submission due on 02.01.2025.
· Project 3: CIL (Coal to SNG) – CIL and BPCL signed MoU for coal to SNG project at Chandarpur, Maharashtra on January 2, 2025. Land of 550 acres and Niljai Extn. OC- Wani area mine has been identified.
Other Projects –
· NLCIL (Lignite to Methanol) – Project located at Nevyeli, Cuddalore, Tamil Nadu. Land of 144 acres identified for the project. LEPC-1 tender for Gasification block done on 22.10.2022, however was cancelled on 01.04.2024 due to high quoted price. EIL appointed as PMC. Revised DFR prepared by EIL.
· New Era Cleantech Solution (Category-III) -setting up Coal to Ethanol Project (56.7 KTPA) at Maharashtra.
9.2. Renewable Energy Initiatives: -Solar Projects
Coal companies are increasingly investing in solar power to diversify their energy portfolios and align with clean energy goals. This strategic shift is evident through their achievements and future targets, reflecting a commitment to renewable energy and reducing carbon emissions.
Achievements Till FY’24: NLCIL has commissioned 1380 MW of solar power, CIL has achieved 83 MW, and SCCL has established 235 MW. Collectively, these efforts have resulted in a total of 1698 MW of solar power, marking significant progress in the transition towards renewable energy.
Targets for FY’25: Looking ahead, NLCIL plans to add 300 MW, CIL aims for 455 MW, and SCCL targets 112 MW. This brings the total target to 867 MW for FY’25. These ambitious expansion plans underscore the companies’ dedication to meeting increasing demand and advancing sustainability goals.
Long-term Goals up to FY’30: In the long term, NLCIL aspires to reach 7.0 GW, CIL plans for 5.0 GW, and SCCL targets 2.4 GW. The combined long-term target is an impressive 14.4 GW. These goals highlight a strategic shift towards substantial investments in renewable energy, positioning these coal companies as leaders in the clean energy transition.
Under PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana has planned to saturate all Office Buildings/Residential complexes of govt buildings by December, 2025. Projection for coal PSUs are follows.
Sl. No.
Company
Planned Roof Top Capacity FOR 100% Saturation (MW)
Installed Roof Top Capacity till Oct’2024
Planned Roof Top Capacity for 100% Saturation (To be Commissioned by December 2025
1.
CIL
41.905
15.425
26.48
2.
SCCL
31.33
0.184
31.15
3.
NLCIL
05
1.2
3.8
Overall Total (MW)
78.235
16.809
61.43
9.3. Thermal Power Plants
· SECL-MPPGCL JV,1X660MW (Madhya Pradesh): The SECL-MPPGCL joint venture in Madhya Pradesh, located in the Anuppur District, has a power generation capacity of 1×660 MW. The project’s cost is estimated between Rs.5600 Cr. to Rs.7254 Cr., with commissioning anticipated by August 2028. The ownership structure of the venture allocates 49% to SECL and 51% to MPPGCL.
· MCL-MBPL, 2X800MW(Odisha): Mahanadi Basin Power Limited’s project as a wholly owned subsidiary of CIL, in Odisha, located in Sundergarh District, boasts a capacity of 2×800 MW. With a project cost totaling Rs.15947+/ (-)20% Cr. Unit-1 is anticipated to be commissioned by Dec, 2029.
· Ghatampur Thermal Power, 3x660MW Plant (Uttar Pradesh): Neyveli Uttar Pradesh Power Limited (NUPPL) is a joint venture between NLC India and Uttar Pradesh Rajya Vidyut Utpadan Nigam Limited. It is located in Ghatampur, Kanpur Nagar, Uttar Pradesh. The equity participation is divided between NLCIL and UPRVUNL in a ratio of 51:49. Unit #1 Commissioned in December, 2024. Unit #2 expected in March, 2025 and Unit #3 in June, 2025.
· NLC Talabira Thermal Power Project, 3x800MW (Odisha): NLCIL Board has granted in-principal approval for the establishment of a coal-based pithead power station with a capacity of 3×800 MW at Tareikela, located in the Jharsuguda District of Odisha. The estimated project cost is Rs.27,213 crores. The Government of Odisha has provided administrative approval for the acquisition of private land. The foundation stone was laid by the Prime Minister on February 3, 2024. Currently, site preparation work is underway. The anticipated completion dates for the units are as follows: Unit #1 in March 2029, Unit #2 in September 2029, and Unit #3 in March 2030.
9.4. Critical Minerals
Critical minerals are essential for modern technologies, including batteries, renewable energy systems, and electronics. Coal companies are exploring opportunities in this sector to diversify their operations and tap into new revenue streams.
· Asset Acquisition within India: Coal companies are planning to participate in the Critical Mineral Auction Tranche II, floated by the Ministry of Mines, to acquire assets within the country. This strategic move aims to secure essential resources for future technological advancements and energy solutions. CIL has already acquired one graphite block namely Chhote Khatali.
· Overseas Acquisitions: Companies are also exploring international opportunities, with NDAs signed for potential asset acquisitions abroad. The goal is to secure a diverse supply of critical minerals from global sources, ensuring a steady and reliable flow of resources.
· Partnerships: Collaborations with international partners and experts are being pursued to facilitate the acquisition and development of critical mineral assets. These partnerships are crucial for navigating the complexities of global mineral markets and securing strategic resources.
9.5. Pump Storage Plants
Pump storage plants are essential for energy storage, providing a method to balance supply and demand on the grid while supporting the integration of renewable energy sources. By storing energy, these plants ensure a stable and reliable power supply, playing a critical role in modern energy systems. Total 26 (CIL-24, NLCIL-1 & SCCL-1) PSP sites have been identified. Out of this, 05 projects of CIL will be implemented in 1st phase. To ensure the viability and strategic alignment of pump storage projects, Tata Consultants have been appointed to conduct comprehensive feasibility studies. These studies will assess various factors to confirm the feasibility of proposed projects.
- Policy for Auction of Coal Linkages to Non-Regulated Sector: