BSNL’s Indigenous 4G stack embodies Swadeshi spirit
BSNL’s Indigenous 4G stack embodies Swadeshi spirit

Introduction
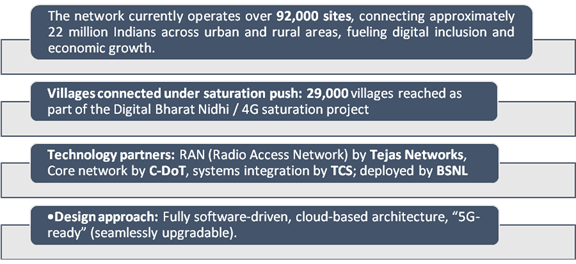
India has marked a historic milestone with the launch of its first fully indigenous 4G (5G-ready) network and the commissioning of nearly 98,000 Swadeshi 4G towers, all powered by homegrown technology. The core network, developed by C-DOT, with Tejas Networks’ Radio Access Network and integration by TCS, exemplifies a major technological breakthrough and the realization of the Government’s commitment to Aatmanirbhar Bharat.
Previously dependent on foreign technology for telecom services like 2G, 3G, and 4G, India responded to the Covid-19 pandemic by building this fully indigenous 4G stack from scratch, demonstrating resilience, rapid innovation, and supply-chain independence. This achievement places India among five nations capable of launching fully homegrown 4G services, reinforcing the swadeshi spirit. BSNL’s cloud-native, 5G-ready 4G stack ensures immediate connectivity while enabling seamless upgrades, nurturing domestic talent, and strengthening supply chains. Complementary government initiatives, including the Bharat 6G Alliance, 100 5G/6G labs, and the Telecom Technology Development Fund are advancing research and innovation, charting a path toward Viksit Bharat 2047 and global leadership in digital technology.
What is 4G?
4G is the short name for fourth-generation wireless, the stage of broadband mobile communications that supersedes 3G (third-generation wireless) and is the predecessor of 5G (fifth-generation wireless).
With 4G download speeds, wireless users can stream high-definition video and audio. 4G also enables wireless broadband, which provides a way for users to get internet connectivity without the need for a fixed, wired connection from an internet service provider (ISP).
4G leverages technologies like LTE, MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output), and OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) for improved bandwidth, network efficiency, and reduced congestion.
Features of the 4G Stack
BSNL’s indigenous 4G services are expected to benefit tribal regions, remote villages, and hilly areas by providing access to quality digital services. This will enable children in rural areas to attend online classes, farmers in distant locations to check crop prices, and patients to consult doctors through telemedicine. Additionally, the initiative will greatly support armed forces personnel by enhancing secure communication through improved connectivity.
Benefits & Impact of the Indigenous 4G Stack
Going beyond 4G: Embracing 5G
The successful deployment of indigenous 4G technology and expansion of 5G is accelerating digital connectivity and strengthening India’s telecom ecosystem for future advancements.
5G Use Cases
Stepping Stone to 6G
The rapid rollout and domestic adoption of 5G are laying the foundation for India’s Bharat 6G Mission, positioning the country as a global leader in future telecom innovation. Currently, the 6G technology is under development phase at international level and is expected to be available by 2030. On March 23, 2023, India’s 6G vision “Bharat 6G Vision” document was released, which envisages India to be a frontline contributor in design, development and deployment of 6G technology by 2030.
Bharat 6G Vision is based on principles of affordability, sustainability and ubiquity (universality). The Department of Telecom has facilitated setting up of ‘Bharat 6G Alliance’ which is an alliance of domestic industry, academia, national research institutions and standards organisations to develop action plan according to the Bharat 6G Vision.
Initiatives taken by the government for 6G roll-out
GSMA Mobile Internet Connectivity Index
As per the State of Mobile Internet Connectivity 2025 report (Network Coverage and Infrastructure), the majority of network investment continues to be in deployments of 5G, which has now reached more than half the world’s population (54% or 4.4 billion people), with more than 700 million additional people covered in 2024. More than half of that growth was driven by India, which has achieved just over 80% population coverage for 5G.
During 2024, monthly 5G traffic in the country increased threefold and now accounts for 36% of India’s total mobile traffic, compared to 15% in 2023.
Global Context
According to statistics by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU),
Some key findings from ITU in 2024 include:
Conclusion
The rollout of the indigenous 4G stack marks a defining step in India’s digital transformation. It blends technology, self-reliance, and inclusive growth, bringing millions online, creating jobs, and proving India’s capability to design and deploy world-class telecom solutions. With its future-ready, 5G-ready architecture and export potential, this initiative strengthens India’s position as a global digital powerhouse. Complementing this progress, ongoing government initiatives for 5G expansion and the development of 6G technologies through the Bharat 6G Alliance and related programs ensure that India is well-positioned to lead in next-generation telecom innovation. Together, these efforts pave the way towards Viksit Bharat 2047, where India not only builds for itself but also empowers the world in the era of 5G, 6G, and beyond.
References:
Jyotiraditya M. Scindia (X Handle)- https://x.com/JM_Scindia/status/1971847954827755710
PMO:
Ministry of Communications:
GSMA (Global System for Mobile Communications Association):
International Telecommunication Union:
TechTarget: https://www.techtarget.com/searchmobilecomputing/definition/4G