Architect of Pollen development & Seed formation identified
Architect of Pollen development & Seed formation identified
Scientists have identified a novel gene that plays a crucial role in the development of stamens (male reproductive structure) including pollen grain and seed formation, in Arabidopsis flowering plants related to cabbage and mustard. The study opens up new possibilities for improving crop fertility and seed production.
Pollen formation represents a very important developmental stage in plant life cycle. It represents the male gametophyte and its role is to deliver the genetic material to the embryo sac. The production and transfer of viable pollen grains to the stigma, germination of the pollen grains, growth of the pollen tubes down the style, and effective fertilization are necessary for the formation of a successful seed set. Thus, understanding the pollen development process not only elucidate the basic mechanism of sexual reproduction of flowering plants but also add valuable information for subsequent manipulation in crop production.
“Pollen germination speed” and “pollen tube growth” are the two important characteristic features of healthy pollens that have evolved with the evolution in flowering plants (Angiosperms). The rapid growth of the pollen tube through the style to reach ovary, is a pre-requisite for fertilization in flowering plants. Since many pollen tubes grow through the style, the reproductive success of a pollen grain is determined by its rate of pollen tube elongation.
It has been shown that maturation of pollen grain with proper structure and composition of cell wall determines its interaction with the stigma as well as its germination ability for successful fertilization. Thus, it is important to understand the molecular mechanisms responsible for pollen development, pollen hydration and pollen germination- factors that are responsible for the formation of a mature viable pollen grains.
Recent investigations on pollen development by Prof. Shubho Chaudhuri’s lab at Bose Institute, Kolkata, an autonomous institution of Department of Science and Technology, identified a novel gene named HMGB15, a non-histone protein that restructures chromatin, plays a crucial role in the development of stamens (male reproductive structure) in Arabidopsis.
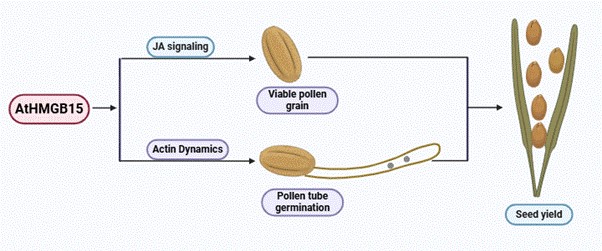
A mutation in this gene, causes partial male sterility in plants. The mutant plants exhibit low pollen grain viability, defective pollen wall patterning, retarded pollen tube germination rate, shorter filaments that are unable to reach the stigma resulting in reduced seed production. The abnormalities in the mutants are due to the disruption in gene regulatory networks important for pollen development, maturation and pollen tube germination.
Molecular analysis indicated that several developmental pathways like biosynthesis of phytohormone jasmonic acid (JA), apoptosis of tapetal cells and actin polymerization dynamics have been severely affected in the HMGB15 loss of function mutants.
Understanding this mechanism on a model organism used for studying plant biology, not only sheds light on the intricate biology of plants but also opens new possibilities for improving crop fertility and seed production. The studies have been published in reputed plant journals namely, Plant Physiology (Sachdev et al., 2024) and Plant Reproduction (Biswas et al., 2024). Financial support for this work was provided by SERB, India.