AI@Work: Driving Productivity, Jobs, and Innovation
AI@Work: Driving Productivity, Jobs, and Innovation
Key Takeaways
AI: Engine of Growth
From code to creativity, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rewriting the rules of growth, powering industries, transforming jobs, and propelling India into the future. AI is becoming kinetic enabler for the growth of India’s digital economy, investments and jobs.
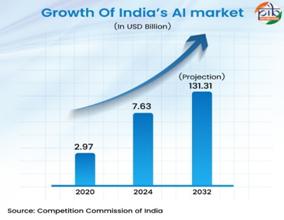
India is in the first group of AI-ready nations, with systematic progress across all five layers of the AI architecture applications, models, chips, infrastructure and energy. The report published by CCI (Competition Commission of India) cites that the global market size of AI has increased from USD 103.6 billion in 2020 to USD 288.8 billion in 2024. During the same period, the AI market in India has expanded from USD 2.97 billion to USD 7.63 billion. The Indian AI market is expected to grow to USD 131.31 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 42.2%.

The Government of India is actively promoting technological development in India aligned with AI led transformation. This has come to pass through focused initiatives in research, innovation, and skill development while ensuring “Welfare for All, Happiness for All”. The steps taken by government make certain that technology enhances productivity, generates new employment opportunities, and strengthens the nation’s global competitiveness.
India’s Emerging Leadership in Global AI
Global benchmarks indicate that India is emerging as a relatively well-positioned economy for Artificial Intelligence readiness.
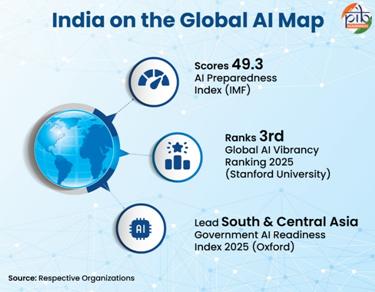
India’s Standing in Global Indicators
Index
India’s ranking
What it signifies?
Stanford University’s 2025 Global AI Vibrancy
3rd, behind the U.S. and China
Growth in R&D, talent, and economy
IMF’s AI Preparedness Index
India gained the score of 49.3, which is higher than the 42.1 average for other emerging and developing economies
India is better positioned to adopt and benefit from Artificial Intelligence.
Oxford’s Government AI Readiness Index 2025,
India continues to lead South and Central Asia and ranks 27th with a score of 66.55
India’s strong year-on-year progress on the basis of flurry of measures and efforts throughout 2025.
Together, these global indicators highlight India’s rising capacity to leverage artificial intelligence as a driver of productivity, inclusion, and long-term economic transformation.
India’s Strategic Edge in the Age of Artificial Intelligence
India’s global AI readiness is underpinned by a unique combination of a young, digitally skilled population, robust digital public infrastructure, and a fast-growing startup ecosystem. These foundational strengths provide India with a durable strategic edge in developing, deploying, and governing AI at scale.
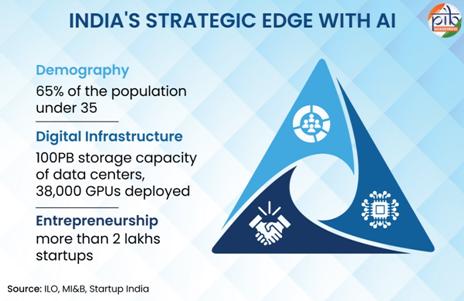
Demography
India has one of the youngest workforces in the world, with over 65% of the population under 35. This large, tech savvy talent base can be trained and adapted for AI driven industries, creating a strong foundation for innovation, digital services, and future ready jobs.
Digital Infrastructure
India’s rapid digital transformation is being underpinned by strong foundational infrastructure, with data centres and widespread internet connectivity emerging as critical enablers of cloud adoption, AI deployment, and data-driven governance across the country.
One of the central pillars of India’s digital infrastructure is the expansion and development of data centres. These centres are crucial for supporting the increasing demand for cloud computing, data storage, and AI/ML applications. The National Informatics Centre (NIC) has established state-of-the-art National Data Centres (NDC) in cities like Delhi, Pune, Bhubaneswar, and Hyderabad, providing robust cloud services to government ministries, state governments, and public sector undertakings (PSUs). At NDC, storage capacity has been expanded to approximately 100PB, including All Flash Enterprise Class Storage, Object Storage, and Unified Storage. Data storage is crucial for training, deploying, and hosting AI models and rapid growth in data centres reduces bottlenecks.
Entrepreneurship
India is witnessing a surge in startups and innovation led enterprises. Over the past decade, the Indian startup ecosystem has recorded unprecedented expansion, with more than 2,00,000 startups recognised by DPIIT across the country. Startups and AI entrepreneurs are the co-architects of India’s future and this growing entrepreneurial ecosystem ensures that AI solutions are locally relevant, scalable, and globally competitive.
AI Start-Ups
In preparation for the India AI Impact Summit 2026, 12 Indian AI start-ups selected under the Foundation Model Pillar engaged in Roundtable chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi, and presented their ideas and work.
These Start-ups are working in a diverse set of areas including Indian language foundation models, multilingual LLMs, speech-to-text, text-to-audio and text-to-video; 3D content using generative AI for e-commerce, marketing, and personalized content creation; engineering simulations, material research and advanced analytics for data-driven decision-making across industries; healthcare diagnostics and medical research, among others.
AI as an Opportunity: Labour Market Evolution
While AI is frequently viewed as a workforce disruption worldwide, it offers India a unique opportunity to drive inclusive growth and innovation.
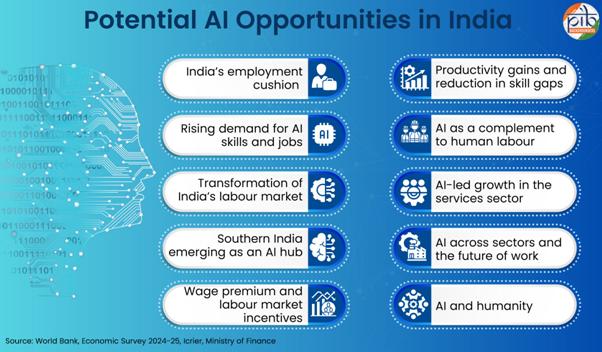
Rising demand for AI skills and jobs
The demand for AI-related skills is rising rapidly. In South Asia, between January 2023 and March 2025, the proportion of AI-related job postings more than doubled, increasing from 2.9% to 6.5% of all vacancies. During the same period, demand for AI skills grew 75% faster than non-AI roles, largely driven by high-wage, urban, white-collar employment. Overall, the rapid rise in AI-related jobs highlights a decisive shift toward high skill, urban employment, with India increasingly positioning itself as a significant hub for AI adoption and talent demand.
Transformation of India’s labour market
The rapid growth in AI-related jobs signals a positive transformation in India’s labour market.
It points to the creation of new, high-value employment opportunities across technology, services, manufacturing, and creative industries. As AI adoption expands, demand is emerging for a diverse set of roles, including AI trainers, safety testers, prompt engineers. This diversification is supporting both experienced professionals and new entrants through upskilling and reskilling initiatives under programmes such as Skill India, Digital India, and FutureSkills Prime.
Southern India emerging as an AI hub
According to World Bank’s South Asia Development Update Report, AI-related job opportunities in South Asia are heavily concentrated in India and Sri Lanka, with India accounting for the majority of listings.
In India, 5.8 percent of white-collar 2025 listings required AI expertise, driven by the southern technology corridor including Bangalore (11% share of AI jobs) and Hyderabad (9.57%), followed by Pune (6.95%) in Maharashtra, with Chennai (6.62%) also featuring prominently. ,
Wage premium and labour market incentives
AI-related employment offers significant wage advantages, reflecting strong global demand for emerging skills. As per the World Bank report, jobs requiring digital skills offers an average 12% wage premium, while AI-focused roles command a much higher 28% premium. As AI skills scale up, India is poised to attract higher-value investments and technology-driven projects, creating better-paying jobs and strengthening its position in the global digital economy.
India’s employment cushion
India has an opportunity to reskill its workforce and integrate AI in a gradual, inclusive, and productivity-enhancing manner. Sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, and logistics, where human skills remain essential, are also moving towards AI adoption.
Productivity gains and reduction in skill gaps
Evidence points to significant productivity gains from AI adoption in India. The NASSCOM AI Adoption Index scores India at 2.45 out of 4, with 87% of enterprises actively using AI solutions (December 2025). Based on a survey of 1993 firms by McKinsey, 88% of organisations surveyed in 2025 reported that they are utilising AI in at least one of their business functions. Studies also show that generative AI tools boost productivity by 14% overall and by 34% among new or lower-skilled workers, helping close skill gaps while improving efficiency and customer experience.
AI-led growth in the services sector
The services sector, contributing about 55.3% of India’s Gross Value Added (GVA) in 2024–25, remains the backbone of the economy. Key industries such as IT, finance, healthcare, education, and communications are rapidly integrating AI, creating opportunities to boost productivity, innovation, and sustainable business practices. Building on these strengths, Indian firms are well positioned to enhance global competitiveness through AI adoption.
AI and humanity
AI is increasingly shaping the future of work in India by augmenting human capabilities and expanding high-value employment opportunities while ensuring humans remain central to decision-making and creativity. AI is best positioned to augment human work rather than replace it, especially in complex and context-rich tasks.
AI is expected to enhance productivity, enables workers to focus on creative, analytical, and interpersonal roles and foster inclusive growth by enabling humans and machines to work together, rather than replacing human labour. India’s tech and AI ecosystem already employs over 6 million people and continues to grow, reflecting the nation’s commitment to balancing AI and humanity in its workforce strategy by supporting job transformation instead of job displacement. ,
AI across sectors and the future of work
Beyond services, AI’s transformative potential spans manufacturing, production and supply chains, and customer-facing activities through greater efficiency and personalization. Its broad adoption can expand employment opportunities, reshape the labour market, and promote continuous skill upgradation. This supports a dynamic and inclusive workforce that effectively combines human expertise with technological advancement.
Transforming the Nature of Work with AI
India is strategically advancing Artificial Intelligence. This exhibits the need of democratisation of technology which Indian government is achieving through a series of national programmes and upskilling initiatives that aim to make technology a driver of productivity, inclusion, and employment.
NITI Aayog, in its report “The Opportunity for Accelerated Economic Growth”, highlighted that one of the key potential outcomes of AI-led value creation is India’s ability to progressively narrow the AI skill gap with leading countries by 2035. Similarly, an IMF report has observed that one in every 10 job postings in advanced economies and one in every 20 job postings in emerging market economies now require at least one new skill, underscoring the growing pace of skill transformation in the labour market.
This can be achieved through the development of a skilled workforce, the strengthening of research capabilities, and active contributions to AI models and innovation. The trend underscores the growing imperative for continuous skill upgradation to remain relevant in an evolving world of work. Recognising this shift, India is actively equipping its skilled labour force for the age of Artificial Intelligence through a series of targeted skill development initiatives.
National Programmes
Under the Viksit Bharat Vision 2027, AI is envisioned as a key driver of digital transformation. By integrating AI across industries, India aims to enhance workforce productivity, create new employment opportunities, and bridge skill gaps. This approach will empower both high-skilled and entry-level workers, ensuring equitable participation in the evolving digital economy.
Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) of India envisioned the National Program on Artificial Intelligence. The program serves as the overarching framework for fostering AI adoption to promote inclusion, creativity, and adoption for social impact. Four pillars of the program are:
Aligned with the principle of #AIforAll, the government is emphasizing self-learning online program for each life stage, to acquaint everyone with digital transformation. The program is divided into two sections, i.e., AI Aware, and AI Appreciate.
 The BHASHINI initiative, leveraging AI for 36+ language with 1.2 million+ mobile app downloads, is breaking communication barriers in the digital economy. This enhances workforce participation, particularly for those in non-English speaking regions, and empowers local entrepreneurs and digital workers.
The BHASHINI initiative, leveraging AI for 36+ language with 1.2 million+ mobile app downloads, is breaking communication barriers in the digital economy. This enhances workforce participation, particularly for those in non-English speaking regions, and empowers local entrepreneurs and digital workers.
As per the Economic survey 2025-26, an ‘AI Economic Council’ is intended to operate to calibrate the pace of AI adoption within the country. The council must ensure that deployment of ‘Artificial Intelligence’ does not come at the cost of ‘Human Intelligence’. They will operate as a coordinating authority that is responsible for aligning technology deployment with the evolution of India’s education and skilling infrastructure, while navigating resource constraints and developmental priorities.
Together, these programmes are reshaping the nature of work in India, positioning the nation to harness AI for productivity, inclusion, and sustainable job creation in the evolving digital era.
Skill Development Initiatives
As of December 2025, SOAR (Skilling for AI Readiness) initiative enrolled 1.34 lakh students and teachers. Under this initiative, AI-readiness courses are being delivered in partnership with Microsoft, HCL Technologies and NASSCOM to equip students and educators with foundational and applied AI skills.
The President of India also launched the #SkilltheNation challenge under the SOAR (Skilling for AI Readiness) to expand public awareness around AI readiness.
Eight Thematic Areas of YUVAi
Krishi (Agriculture)
Aarogya (Health)
Shiksha (Education)
Paryavaran (Environment)
Parivahan (Transport)
Grameen Vikas (Rural Development)
Smart Cities
Vidhi aur Nyaay (Law and Justice)
As of December 2025, the government is supporting 500 PhD scholars, 5,000 postgraduates and 8,000 undergraduates for AI related work. 27 IndiaAl Data and AI Labs are established in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities through NIELIT to conduct coursework in AI, data curation, annotation, cleaning and applied data science. Also, 174 lTIs and Polytechnics across 27 States/UTs have been approved to set up additional IndiaAl Data and AI Labs.
Towards a Future-Ready and Inclusive Workforce
India is at the forefront of an AI-led transformation, where technology is driving productivity, innovation, and job creation. With robust digital infrastructure, a young workforce, and progressive policies, the nation is well-positioned to leverage AI for inclusive growth. This integrated approach of government ensures that AI enhances employability and bridges skill gaps across sectors. By aligning technology with inclusion, India is shaping a resilient and future-ready workforce.
References
Competition Commission of India
https://www.cci.gov.in/economics-research/market-studies/details/47/0
Niti Aayog
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2177440
https://niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2025-10/Roadmap_On_AI_for_Inclusive_Societal_Development.pdf
https://niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2025-10/Roadmap_for_Job_Creation_in_the_AI_Economy.pdf
International Monetary Fund
https://www.imf.org/en/blogs/articles/2026/01/14/new-skills-and-ai-are-reshaping-the-future-of-work
PHD Chamber of Commerce and Industry
International Labour Organisation
https://www.ilo.org/media/38031/download
Ministry of Information & Broadcasting
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx/pib.gov.in/Pressreleaseshare.aspx?PRID=2082144
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2216958®=3&lang=1
DD News
Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade
https://www.startupindia.gov.in/content/sih/en/Prabhaav.html
World Bank
https://blogs.worldbank.org/en/endpovertyinsouthasia/labor-market-implications-of-ai-adoption-in-south-asia-in-five-c
Economic Survey
https://www.indiabudget.gov.in/budget2025-26/economicsurvey/doc/eschapter/echap13.pdf https://www.indiabudget.gov.in/economicsurvey/doc/eschapter/echap14.pdf
Ministry of Finance
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=2098048
Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations
https://icrier.org/pdf/ES/ES-Implications_of_AI_on_the_Indian_Economy.pdf
Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology
https://www.digitalindia.gov.in/initiative/national-program-on-artificial-intelligence/
https://www.futureskillsprime.in/
https://indiaai.gov.in/hub/indiaai-futureskills
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2206767®=3&lang=1
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2214120®=3&lang=1
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2198216®=3&lang=1
Ministry of Education
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2184211®=3&lang=1
Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2150228
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2204136®=3&lang=1
Ministry of Labour and Employment
https://sansad.in/getFile/annex/268/AU3299_IiQ1Vk.pdf?source=pqars
President of India
Prime Minister’s Office
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2212390®=3&lang=1
Others
https://www.nber.org/papers/w31161
https://x.com/JM_Scindia/status/2012015160781914541?utm
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2209737&lang=1®=3
https://hai.stanford.edu/assets/files/hai_ai_index_report_2025.pdf
https://hai.stanford.edu/ai-index/global-vibrancy-tool
https://oxfordinsights.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/Government-AI-Readiness-Report-2025-1.pdf
https://cat.eto.tech/?expanded=Summary-metrics
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressNoteDetails.aspx?NoteId=157247&ModuleId=3®=3&lang=1
- National Education Policy (NEP) 2020: The policy emphasizes digital and AI literacy as core competencies across all levels of education. By embedding computational thinking and AI learning into curricula, the policy ensures that India’s next generation enters the workforce ready for the evolving technological landscape.